- Acute Kidney Injury (Acute Renal Failure)
-
- An abrupt loss of kidney function, which is typically caused by a sudden loss of blood flow to the kidneys. The loss of blood flow could be caused by a number of reasons, such as low blood pressure, exposure to harmful substances, inflammation of the kidney, or obstruction to the urinary tract. Although not always fatal, acute kidney injury does have the potential to lead to death. If an individual’s diagnosis of acute kidney injury is severe enough to limit a major life activity, it may gain disability protection.
- HIV/AIDS
- Human immunodeficiency virus is a condition that weakens a person’s ability to fight infections. HIV has a multiple stage infection process. The first stage appears to be a simple viral infection, the second stage is a non-symptomatic stage where the virus quietly destroys the immune system, then finally the immune system is destroyed and the body is left vulnerable to opportunistic infections and diseases. Eventually an individual will suffer from acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) as a result of the HIV infection. This disease can be transferred through blood, semen, vaginal fluid, pre-ejaculate, or breast milk. HIV/AIDS is a life altering disease and is considered to be a disability that limits major life activity.

- Amputation
- Surgical removal of all or part of a limb or extremity such as an arm, leg, foot, hand, toe, or finger. Amputation is unique because it can be the result of hundreds of causes from trauma to various medical illnesses such as gangrene. Whatever the cause for an amputation, it is not always considered a disability. Minor amputations of toes or fingers may not limit an individual’s life in any way. However, more severe amputations of perhaps a hand or limb would have a more substantial impact on one’s ability to work and enjoy life. Similar to most conditions, amputation gains disability protection depending on the severity of the case.
- Anemia (Anaemia)
- A condition in which an individual does not have enough hemoglobin to carry sufficient oxygen to the various tissues in the body. Symptoms are often slow and random. Individuals can experience exhaustion, weakness, shortness of breath, inability to exercise, confusion, loss of consciousness, and increased thirst. Anemia is one of the most common blood disorders in the world and affects nearly 1 billion people. Like many diseases, anemia has a very broad range of severity levels and will only be given disability protection if it is severe enough to limit a major life activity. An example of severe Anemia would be Hemolytic Anemia, which is a disorder that results in premature destruction of red blood cells.
- Allergies (Severe)
- Severe allergies are those allergies that go beyond a mere seasonal sneeze and congestion. It goes beyond avoiding certain foods. Severe allergies are so severe that they interfere with an individual’s quality of life. Allergies that are so bad that an individual needs to take a day off from work to cope with symptoms or is unable to step outside due to a high pollen count. In these cases, it is likely that a person’s allergies will be considered a disability, since they will limit major life activities such as going to work or stepping outside of their own house for any reason.
- Asthma
- Asthma is a chronic long-term lung disease that inflames and narrows the airways. This leads to a wheezing period, where individuals will cough and have difficulty breathing. While many individuals outgrow asthma, some adults still suffer from this lung disease. Furthermore, frequent attacks can create an interference with leading a normal life. For example, some individuals, in spite of treatment, will have attacks that occur once every couple of months, sometimes more frequently. Furthermore, some attacks can be so severe that they lead to hospitalization. It is for these reasons that severe cases of Asthma are given disability protection.

- Avascular Necrosis – Osteonecrosis – Aspetic Necrosis – Ischemic Bone Necrosis –
- A condition where bone components die due to an interruption in blood supply. Without the blood, the bone tissue will die and lead to an eventual bone collapse. This illness can occur in any part of the body. Disability status can be gained from this condition depending upon many factors such as location, size, treatment, etc.
- Meningitis
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the protective membrane covering the brain and spinal cord. It is considered a deadly disease due to its proximity to important areas of the body. In adults, severe headaches, inflexible necks, sudden fever, and altered mental status are all signs of meningitis. In some cases, this condition may lead to death. This condition can be resolve quickly or in some situations may cause a serious physical, mental, and financial burden. Depending on the severity of the conditions, it is possible to qualify for disability benefits.
- Encephalitis
- Encephalitis is a sudden onset of an inflammation of the brain. Symptoms include headache, fever, confusion, drowsiness, fatigue, seizures, convulsion, stroke, and memory problems. This condition can be a viral infection, bacterial infection, limbic (focused in the limbic system of the brain), autoimmune, etc. This condition comes in many forms and many severities. Depending upon the seriousness, duration, cost, and impact on an individual, this condition can qualify for disability protection.
- Seizures
- Seizures are the result of abnormal electrical activity in the brain. Some seizures can go completely unnoticed, while others can lead to loss of consciousness and convulsing. Seizures can be caused by head injuries, stroke, low blood sugar, withdrawals, cancer, or other reasons. Whether seizures would be considered a disability depends on their underlying causes, frequency, duration, intensity, and other factors. If an individual’s condition is determined to be severe enough, they will be given disability protection.
- Burns
- Burns are a type of injury that can be caused by the cold, heat, electricity, friction, chemicals, or radiation. Most burns are superficial and have no long term side effects. However, more serious burns, such as third-degree burns and fourth-degree burns, require hospitalization. These burns involve all of the skin’s layers and go as deep as the muscles, even the bone. They often result in a loss of the burnt skin and can leave an individual heavily mutilated. Furthermore, the skin may never fully heal and can become stiff, restricting movement. Severe cases can also render individuals incapacitated for long period of time. If the burn is severe enough, it may be considered a disability.
- Bursitis
- The bursa is a sack filled with lubricating fluid located between the tissues such as bone and muscle. This sack decreases friction between the various tissues. Bursitis is an inflammation of this sack, which depending on the severity, can lead to pain and, in some cases, loss of movement. If an individual’s bursitis interferes with work or limits another major life activity, it will likely be considered a disability and be given protection.
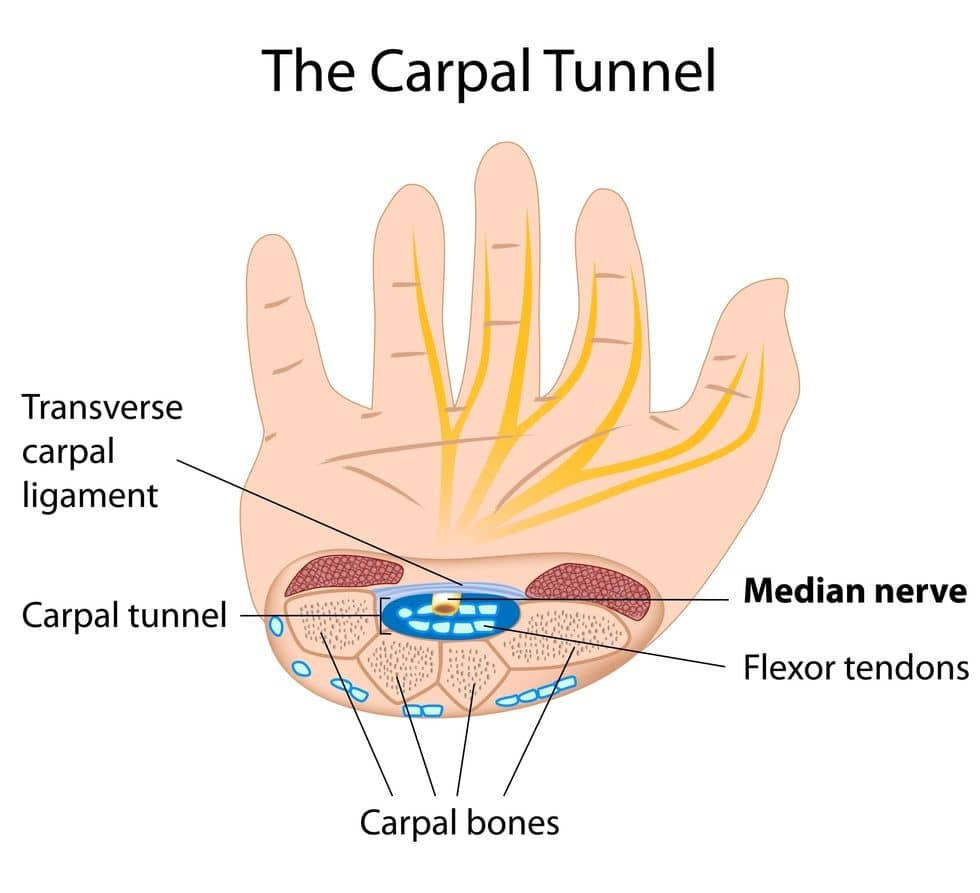
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition where pressure is put on the median nerve causing numbness, tingling, or weakness in the hand. Can lead to serious muscle damage and loss of function of the hand. Onset of carpal tunnel syndrome tends to be gradual, ultimately leading to loss of control. The inability to use one’s hands limits potential to work, perform daily activities, and will interfere with overall enjoyment of life. It is for these reasons that carpal tunnel syndrome, depending on its severity, will likely be given disability protection and status.
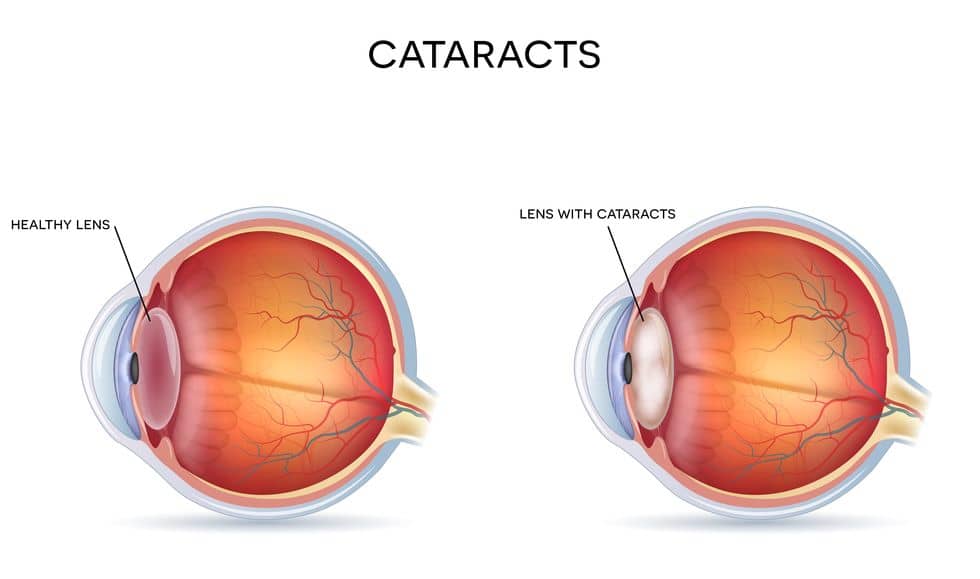
- Cataracts
- Cataracts are a clouding of the lens in the eye leading to a decrease in vision. This can lead to trouble driving, reading, seeing at night, and recognizing faces. Furthermore, severe cases can lead to blindness. This condition may also lead to depression. Depending on the severity of the condition and its ability to be resolved, it may be given disability protection.
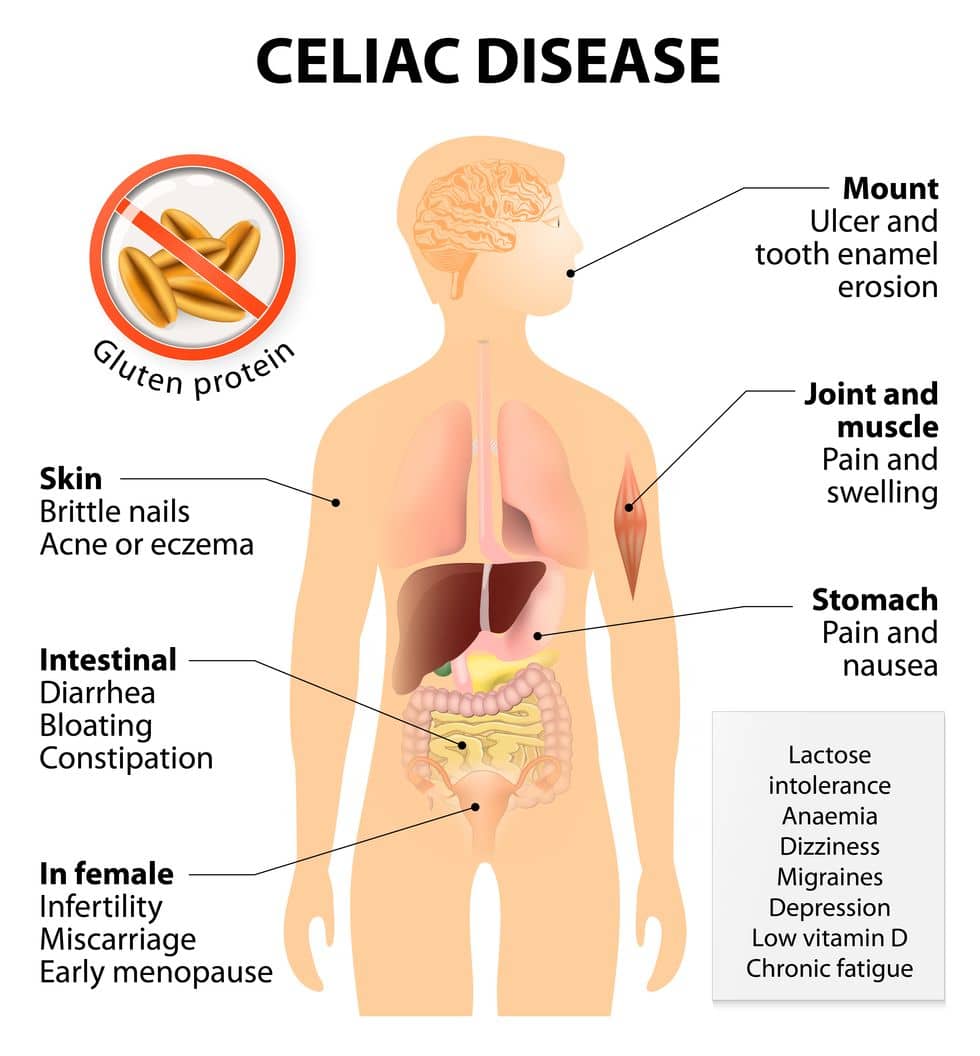
- Celiac Disease (Coeliac Disease)
- Celiac disease is an autoimmune disorder affecting the small intestine. Essentially, within the body there is an issue with digesting gluten, a protein in foods like bread, crackers, and pasta, affecting the absorption of nutrients. Typical symptoms are diarrhea, abdominal distention, loss of appetite, and failure to grow. The current treatment is a very strict gluten-free diet. The most common form of celiac disease is not likely to be given disability protection, but if an individual suffers from a particularly severe case, it may be possible to gain protection.
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
- There is no clear cause or indicator of chronic fatigue syndrome. Some medical professionals believe that it may be caused by a variety of factors. Symptoms include fatigue, loss of memory or concentration, unexplained pain, headache, non-refreshing sleep, and extreme exhaustion following mental or physical exercise. There is no cure and sleep does not assist in any way. If an individual is diagnosed with this illness and it interferes with their major life activities, such as work, this syndrome is very likely to gain disability protection.
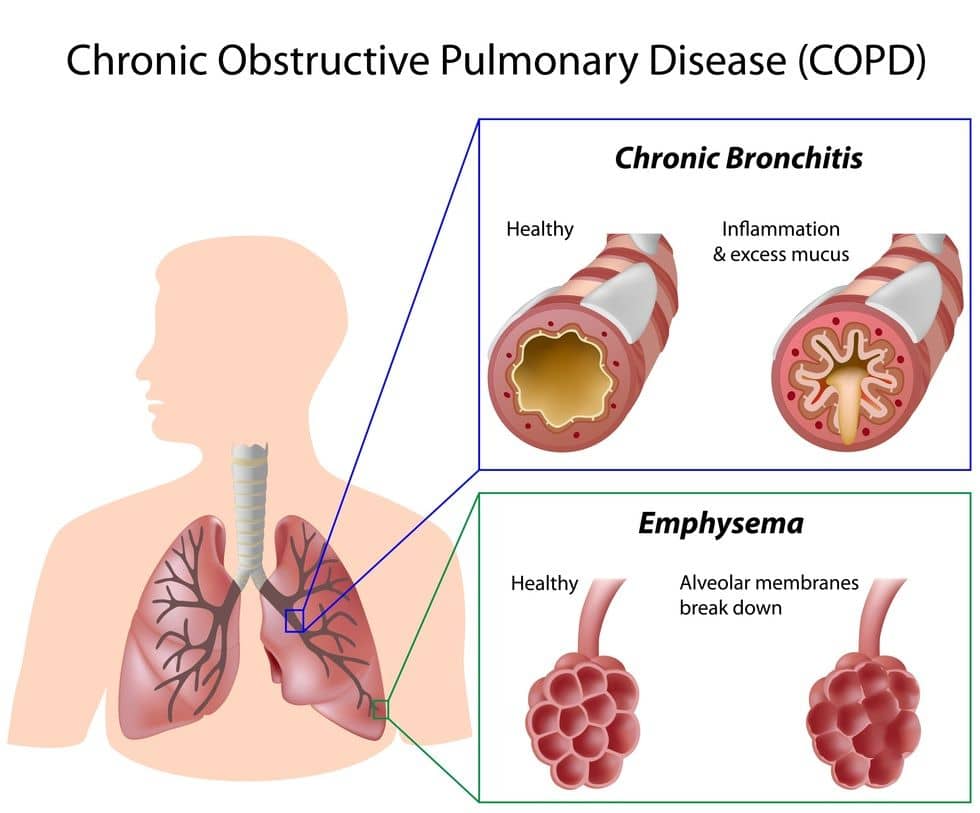
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
- COPD is an obstructive lung disease that is characterized by poor airflow, which gradually worsens over time. Main symptoms include shortness of breath and a chronic cough with mucus production. There is no known cure for COPD and individuals that have it can only hope to slow down its progression. Depending on the severity of the case, this disease is likely to gain disability protection. Constantly coughing up flem and mucus can be very disruptive in both social and professional situations. Examples of COPDs are chronic bronchitis and emphysema.
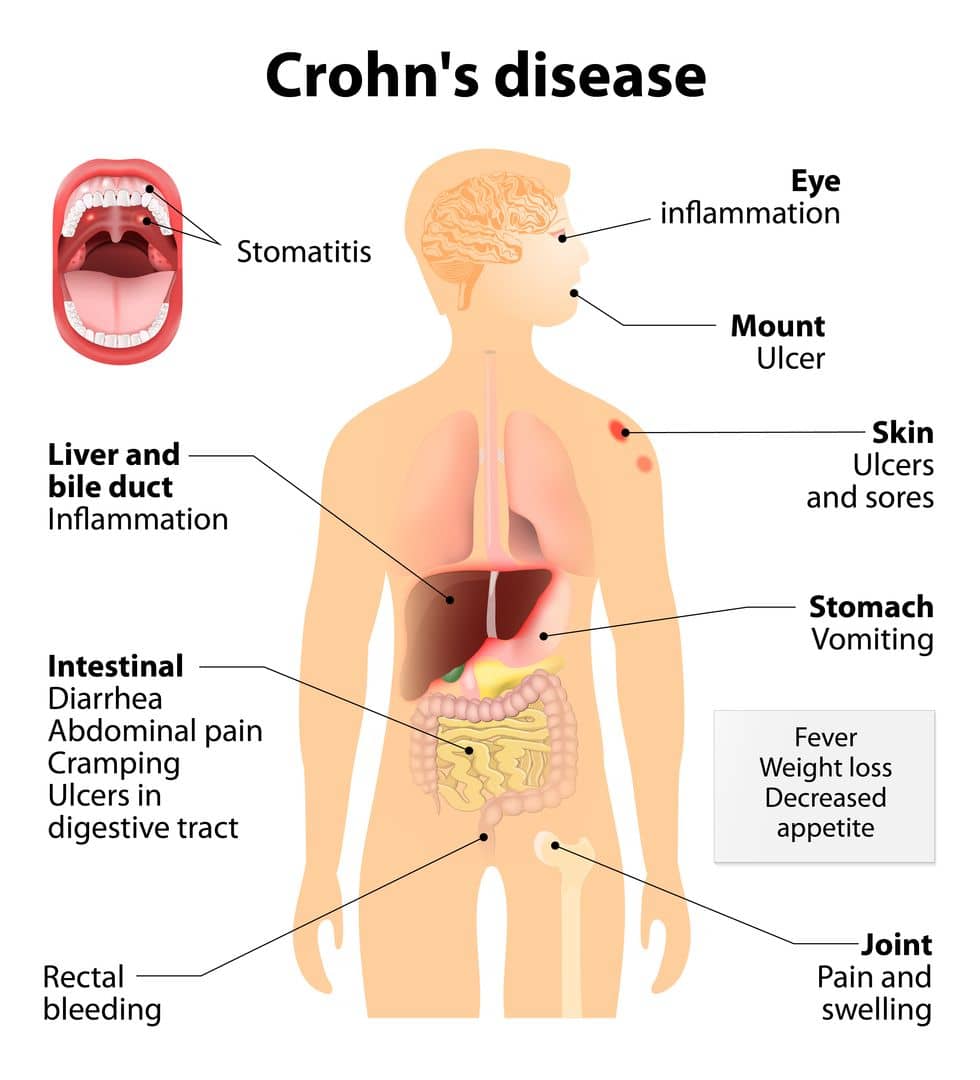
- Crohn’s Disease
- An inflammatory bowel disease that leads to increased bathroom usage, abdominal cramps, fever, and bloody diarrhea. This disease can impact any part of the gastrointestinal tract, sometimes it impacts multiple sections of it. This disease not only impacts the gastrointestinal tract, but can also cause skin rashes, cancer, arthritis, anemia, eye inflammation, and exhaustion. Crohn’s Disease can be a major burden on individuals and prevents them from leading stress-free lives. Depending on the severity of an individual’s case, Crohn’s Disease is very likely to gain disability protection.
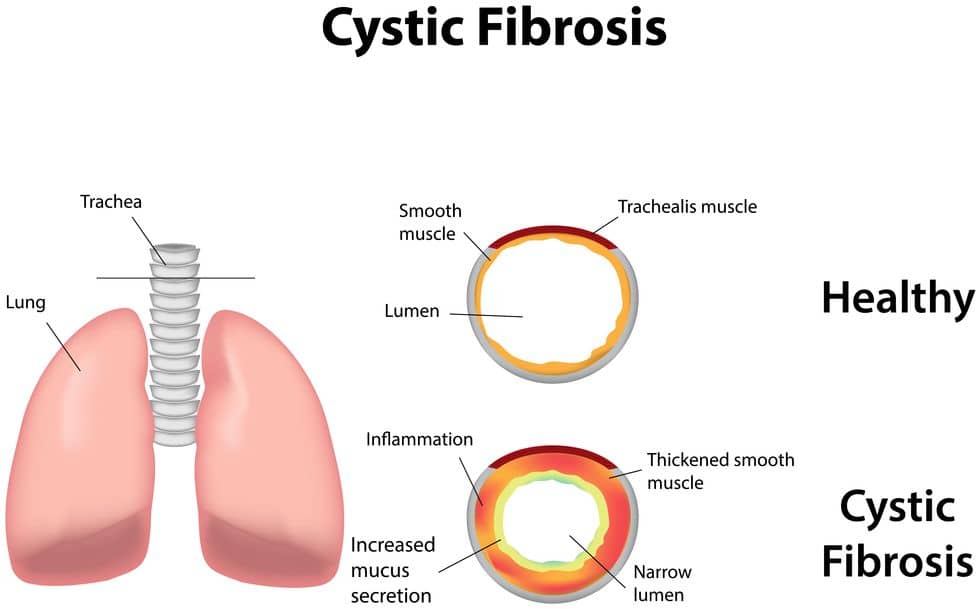
- Cystic Fibrosis
- A genetic disease that affects the glands that produce mucus and sweat, which makes mucus get sticky and thick. This thick mucus builds up in the lungs and makes it difficult to breathe. Symptoms typically include difficulty breathing, coughing up mucus, frequent lung infection, poor growth, finger clubbing, and infertility in males. This condition is an inherited one. Unfortunately, there is no known cure, and this disease will likely receive disability protection, depending on the severity of an individual’s case.
- Type 1 Diabetes
- A condition where the immune system destroys cells in your pancreas called beta cells, which are the cells that produce insulin. Insulin helps move sugar through the body, which the cells use as fuel. When cells do not receive and process the sugar they require, they are starved and die. Symptoms include frequent urination, increased thirst, increased hunger, weight loss, blurry vision, poor healing, and exhaustion. The cause of type 1 diabetes is still unclear, however, depending on the severity of the case, it is very likely to obtain disability protection.
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes is when the body still creates insulin, but the body does not absorb it as well as it should. This is the key difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Type 2 diabetes is more of an insulin resistance rather than an insulin deficiency. Symptoms include things like increased hunger, exhaustion, frequent urination, and weight loss. Long term impact is increased risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, blindness, etc. Type 2 diabetes, like type 1 diabetes, is very likely to gain disability protection.
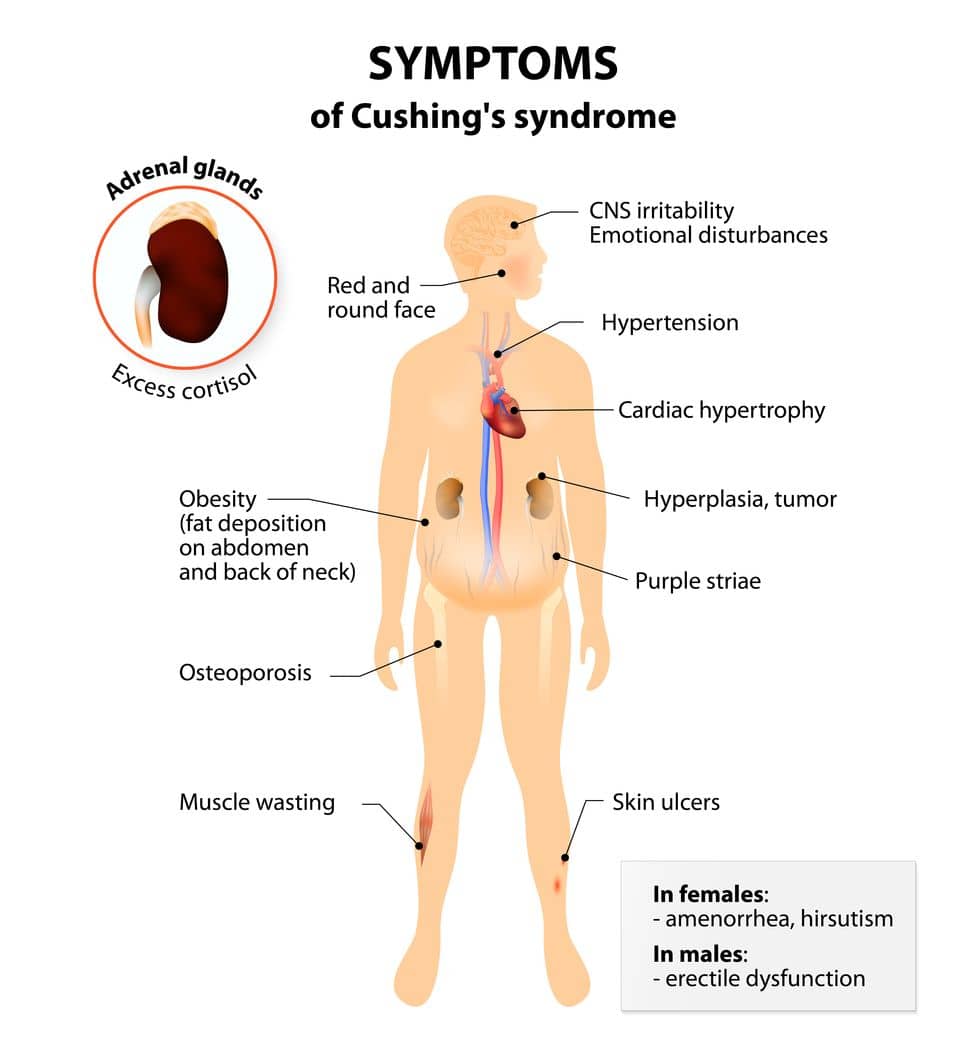
- Cushing’s Syndrome
- This syndrome is the result of overexposure to cortisol. This overproduction of the stress hormone disrupts other bodily functions. Symptoms of this syndrome can be anything from high blood pressure, extra hair growth, osteoporosis, and depression. This condition also leads to Cushing’s Disease, which may lead to tumor growths on the body. While the tumors can be benign, the size and pressure applied to other parts of the body from the tumor can lead to long-term damage. This condition, depending on the severity, may be considered a disability.
- Hyperthyroidism
- A condition that is due to an excessive production of thyroid hormone. Symptoms and severity range greatly, but include weakness, irritability, diarrhea, poor heat tolerance, and fast heartbeat. Symptoms may be more or less severe than those listed above. While not very likely to be considered a disability, those individuals with a very severe case may be able to gain protection.
- Hypothyroidism
- When the thyroid does not make enough of the thyroid hormone, which can lead to changes in the menstrual cycle. Further symptoms include constipation, depression, dry hair and hair loss, dry skin, fatigue, greater sensitivity to cold, low heart rate, swelling of the thyroid gland (goiter), unexplained weight gains, or difficulty losing weight. This condition is dependent on severity and is not likely to gain protection unless symptoms are severe and limit an individual’s ability to perform major life activities.
- Epilepsy
- A group of disorders that have a tendency to result in seizures. This condition can either be extremely debilitating, or people may not know they even have it. In order to determine disability, certain factors such as frequency, duration, and severity of seizures will be considered. If severe enough, individuals will be able to gain disability protection.
- Fibromyalgia
- Fibromyalgia is a medical condition characterized by chronic widespread pain and heightened pressure sensitivity. Symptoms include exhaustion to a point where normal activities are affected, sleep problems, memory issues, bowel or bladder problems, sensitivity to noise, anxiety, depression, and more. The causes of this illness are largely unknown, but it has been thought to be genetic. This condition for the most part will be considered a disability, because its symptoms include an inability to perform normal activities. However, the severity of the condition will still need to be considered and a determination of whether there is a limit on major life activities made before disability protection can be given.
- Gaucher’s Disease
- Gaucher’s disease is a condition that makes it difficult for the body to eliminate certain kinds of fat. When symptoms become severe, they lead to easy bruising, nosebleeds, fatigue, enlarged spleen or liver, which can cause a swollen belly, and bone problems like pain, breaks, or arthritis. Depending on the severity of this condition, it is likely to gain disability protection. However, disability status will likely be reserved for the more serious cases.
- Gout
- Gout is a form of arthritis that can cause sudden waves of burning pain, stiffness, and swelling in a joint. This can result in purplish skin, limited movement, peeling and itching of the skin around the affected joint, and extreme sensitivity to pressure. This condition’s disability status largely depends on frequency and severity of the attacks. If the attacks seem to be happening regularly and are interfering with work and daily life, it is likely to be considered a disability.
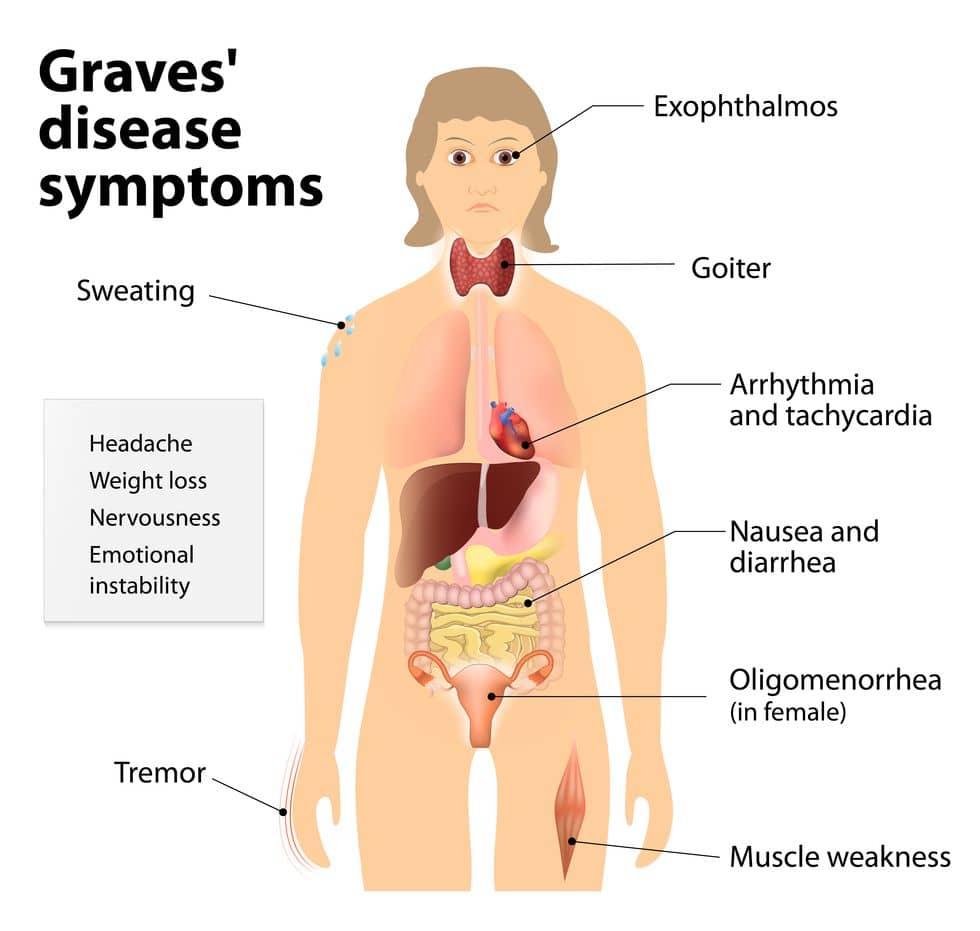
- Graves’ Disease
- The body’s immune system releases abnormal antibodies that trick the thyroid into working overtime. This leads to quickening of metabolism, pounding heart, sweating, trembling, and weight loss typically experienced by people with hyperthyroidism. This condition, depending on severity and duration, may be able to gain disability status; however, this is not usually given.
- Hepatitis A
- An acute infectious disease of the liver that has few or no symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they last approximately eight weeks and include vomiting, nausea, diarrhea, jaundice, fever, and abdominal pain. Furthermore, symptoms can return. Depending on the severity of the condition, it is possible to gain disability protection.
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis B is an infectious disease that impacts the liver. While typically symptoms only last a few weeks, in some more serious cases, Hepatitis B can lead to cirrhosis over a period of several years. Symptoms include loss of appetite, vomiting, body aches, and dark urine. Disability status for Hepatitis B depends on the severity of the condition.
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatitis C is an infectious disease that primarily impacts the liver. While typically symptoms only last a few weeks, in some more serious cases Hepatitis C can lead to cirrhosis over a period of several years. Symptoms include loss of appetite, vomiting, body aches, and dark urine. Disability status for Hepatitis C is heavily dependent on the severity of the condition.
- Hypertension
- Hypertension is high blood pressure that can have severely debilitating symptoms. These symptoms include severe headaches, fatigue or confusion, vision problems, chest pain, difficulty breathing, irregular heartbeat, and pounding in chest, neck, or ears. It is typically caused by both genetics and lifestyle habits. Prolonged high blood pressure can lead to severe coronary artery problems and death.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome
- IBS is a group of symptoms including abdominal pain and changes in pattern of bowel movement. These symptoms occur over a long period of time and consist of diarrhea and constipation. This syndrome severely impacts quality of life and can lead to missed work, anxiety, major depression, and chronic fatigue syndrome. Depending on the severity this syndrome, it is likely to be considered a disability. Furthermore, if an individual is missing work as a result of IBS, it further strengthens its disability status, particularly in California.
- Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (Lupus)
- Lupus is an autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the normal healthy tissues of the body. Symptoms vary, but include joint pain, swelling, arthritis, chest pain, fatigue, fever, hair loss, sensitivity to light, skin rash, and swollen lymph nodes. Lupus can attack any part of the body, which means that some attacks are more severe than others based on their location. Lupus also results in depression and anxiety. Depending on the severity of a case, Lupus is likely to gain disability protection.

- Migraines/Headaches
- Migraines are painful headaches that can lead to nausea, vomiting, and light sensitivity. Migraines are pulsating in nature and can last from 2 to 72 hours. Physical activity is known to increase the pain. Furthermore, individuals can experience adjustments in vision. Causes are a mixture of genetics and triggers. There is no known cure, but sometimes medication can help manage and control the pain. Depending on the frequency and severity, migraines may be considered a disability.
- Mitral Valve Prolapse
- Mitral valve prolapse is when the mitral valve slips backwards into the left atrium, interrupting the normal blood flow of the heart. Symptoms may include chest pain, low body mass index, anxiety, syncope, and low blood pressure. Depending on the severity, and intrusion into an individual’s life mitral valve prolapse may be awarded disability protection.
- Cushing’s Syndrome
- Cushing’s syndrome is the result of too much cortisol building up in your system. This syndrome can result in rounded rosy face, weight gain, especially upper body, thin arms and legs, acne, exhaustion, weak muscles, especially when using your shoulders and hip muscles, high blood pressure, high blood sugar, depression, anxiety, osteoporosis, kidney stones, sleep problems, etc. Depending on an individual’s symptoms and severity, this condition may be awarded disability protection.

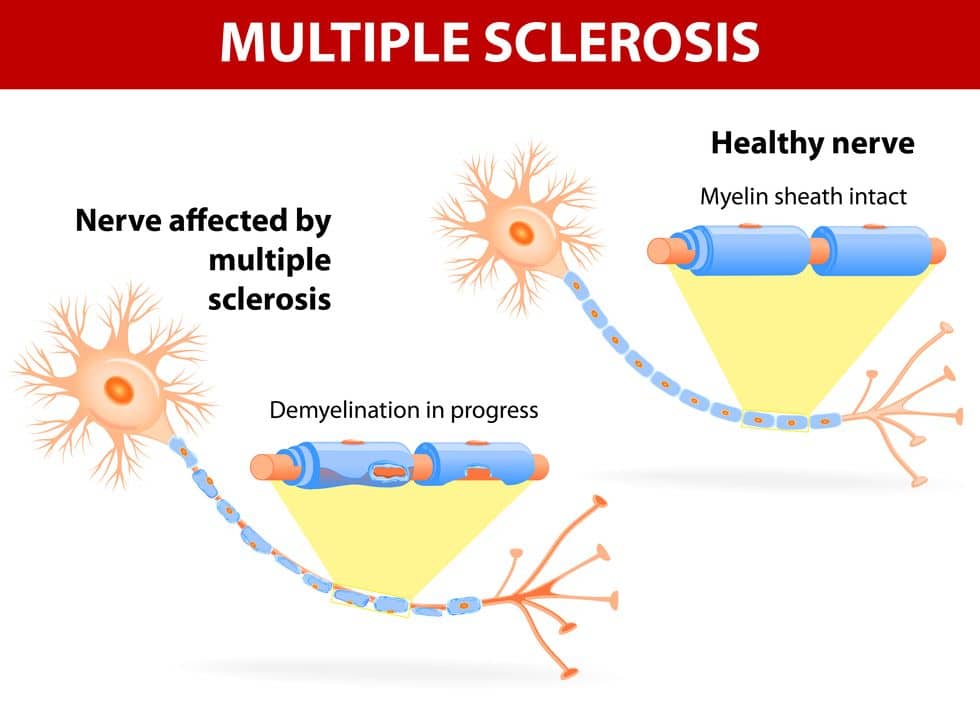
- Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
- MS is a condition where the insulating covers of nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord are damaged. Damage interrupts the ability of the nervous system to communicate, which leads to physical, mental, and sometimes psychiatric problems. MS can be an isolated attack or come in the form of multiple attacks. Typically, symptoms can disappear between attacks, however, there is an onset of neurological problems as the disease progresses. Due to the autonomic, visual, motor, and sensory problems that arise from MS, it will be considered a disability.
- Myositis
- Myositis refers to any condition causing inflammation in muscles, weakness, swelling, and pain. Depending on the severity of the individual’s condition, it may or may not be a disability. The most common form of myositis is myositis ossification, which is a buildup of bone that results from using a body part too soon after trauma. Depending on the severity of the condition and location, this condition may gain disability protection.
- Osteoarthritis
- Osteoarthritis is caused by injury, aging joints, or other causes. It can lead to limited movement, pain, stiffness, and swelling. If individuals suffer from a particularly restrictive case of osteoarthritis, they are likely to earn disability protection.
- Osteoporosis
- Osteoporosis is a condition where the bones begin to thin, resulting in painful fractures. Typically, this condition only impacts adults and only leads to chronic pain following a break. Only severe cases with complications would receive disability protection.
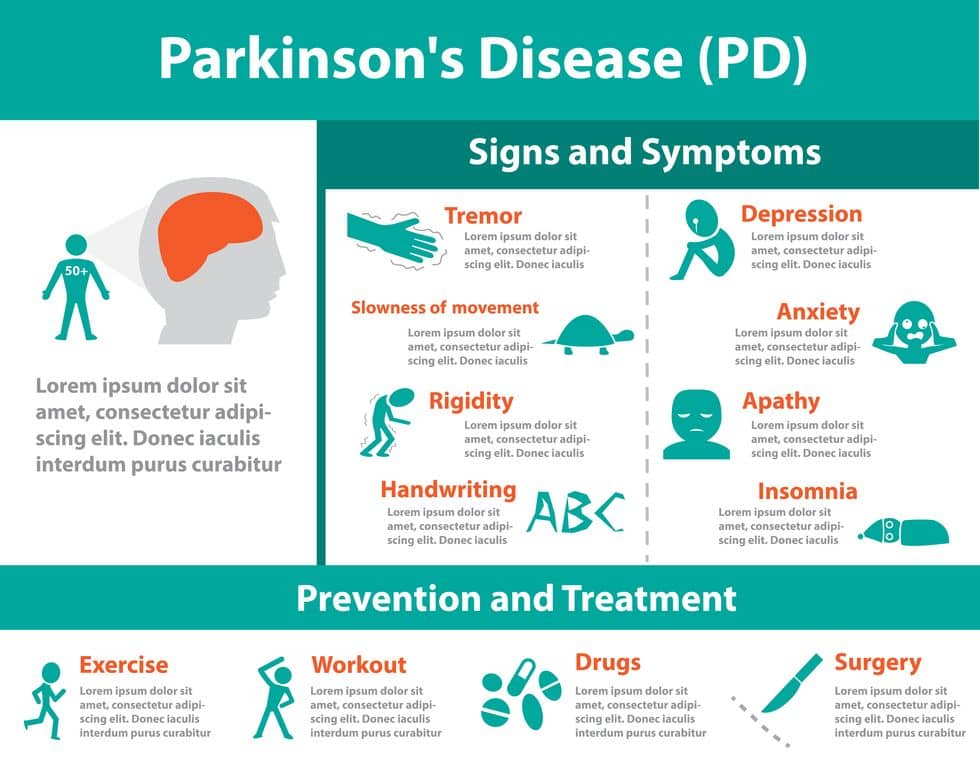
- Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
- PD affects the nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine. Symptoms include muscle rigidity, tremors, and changes in speech. Other symptoms include difficulty walking and other issues relating to the motor system. There are also mental symptoms such as depression and anxiety. Depending on the severity of the condition, PD is very likely to gain disability protection.
- Acute Porphyria
- Acute porphyria impacts the nervous system resulting in severe abdominal pain, chest pain, high blood pressure and heart rate, back pain, loss of sensation, vomiting, constipation, seizures, etc. Depending on an individual’s condition and determined severity, it is possible for this ailment to be given disability protection.
- Psoriatic Arthritis
- Psoriatic arthritis is usually seen in one-third of individuals with psoriasis. This condition is an inflammation of the joints, but can impact other parts of the body as well. Symptoms include severe pain, swelling, or stiffness. This condition can be extremely painful for individuals who have it. Furthermore, due to the severe limitation in movement that results, this condition may be given disability protection.
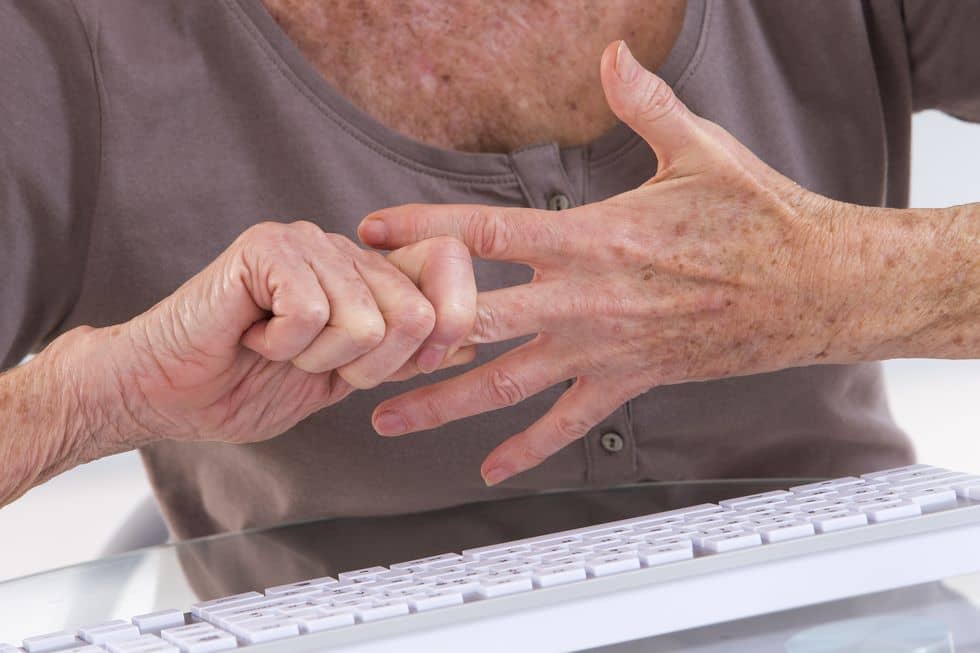

- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a long-term disease whose symptoms can come and go. Symptoms are usually warm, swollen, and painful joints. Essentially, the immune system begins attacking the joints. The goal of treatment is to reduce symptoms and pain. As long as the symptoms are severe enough to prevent working, this condition will qualify as a disability.
- Shingles
- Shingles is a viral infection caused by chickenpox. Symptoms include painful rashes across the entire body. Typically, a rash will develop, which will usually fade in a few weeks. However, some individuals who contract this condition develop ongoing nerve pain, which can last for months. This condition can be extremely painful and prevent any sort of functionality. Typically affects older adults and people with weak immune systems. Based on the severity of the condition, disability protection may be given.
- Ulcerative Colitis (UC)
- UC is a disease that causes inflammation and sores in the lining of the large intestine. In severe cases, an individual can have diarrhea and need to use the bathroom upwards of 20 times in one day. Depending on the severity and impact on one’s life, UC can be given disability protection.
- Bony or fibrous ankyloses
- Fibrous ankyloses is a fibrous connective tissue, which results in a decreased range of motion. Depending on the location and severity of this loss of motion, an individual will likely obtain disability protection for this condition.
- Arachnoiditis
- Arachnoiditis is a chronic pain disorder caused by inflammation of the arachnoid, one of the membranes that surrounds and protects the nerves of the spinal cord. Symptoms usually include severe stinging, burning pain, and neurological problems. There is no cure for this condition, and it can seriously debilitate an individual’s ability to function. Thus, this condition is likely to gain disability protection.
- Spinal stenosis
- Spinal stenosis is an abnormal narrowing of the spine. Symptoms include pain, numbness, Paresthesia, and loss of motor control. With this condition, the spinal canal begins to narrow, cutting off the nerves that pass through it. Due to the loss of movement, this condition is likely to gain disability protection.
- Degenerative Disc Disease (DDD)
- DDD is a narrowing of the vacuum disks within the spine. This leads to the development of chronic lower-back or neck pain. Depending on the frequency and severity of this chronic pain, this condition may be able to gain disability protection status.
- Statutory Blindness
- Statutory blindness is the law’s definition of blindness. This means that a person’s vision is so bad that they are legally considered to be blind. Statutory blindness can develop over time, result from trauma, or be a condition an individual is born with. In order to qualify as statutorily blind, an individual must have a central visual acuity of 20/200 or less in the better eye, with the use of correcting lenses. Instead of a low visual acuity, an individual can also have a visual field whose width in diameter is only 20 degrees. Statutory blindness does qualify for disability protection.

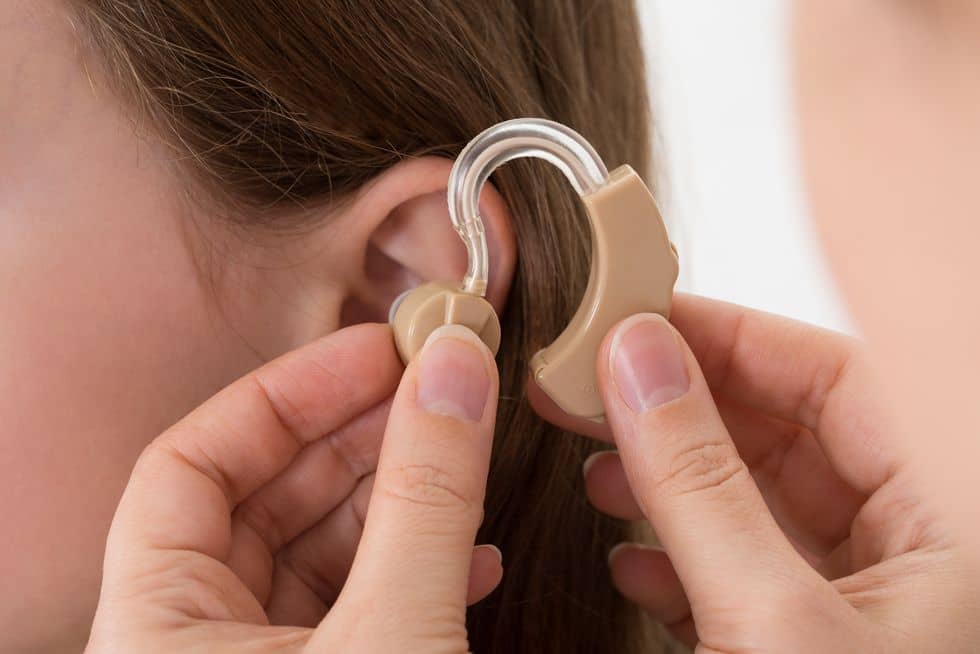
- Hearing Impairment
- A hearing impairment is a partial or total inability to hear. This can be a condition one is born with, or it can be caused by some sort of trauma. An inability to hear is considered a disability and would gain disability protection.

- Pulmonary Hypertension
- Pulmonary Hypertension is an increase of blood pressure in the pulmonary artery, vein, or capillaries. This can cause shortness of breath, dizziness, fainting, leg swelling and other symptoms. Depending on the severity of this condition, it may earn disability protection.
- Bronchiectasis
- Bronchiectasis is a disease in which there is permanent enlargement of parts of the airways of the lung. Symptoms typically include a chronic cough that produces mucus, shortness of breath, chest pain, and nail clubbing. Individuals with this disease often get frequent lung infections. Bronchiectasis is the result of numerous diseases such as pneumonia or tuberculosis. Depending on the severity of each individual’s symptoms, this condition is likely to earn disability protection.
- Chronic Asthmatic Bronchitis
- This condition is a combination of asthma and bronchitis. Both conditions make it difficult to get oxygen into the lungs. Individuals who have this condition experience shortness of breath, wheezing, coughing, chest tightness, and excess mucus production. Based on the severity of the condition and the amount of interference with major life activities, particularly work, this condition will likely be granted disability protection.
- Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)
- CHF occurs when the heart is unable to pump enough oxygenated blood to body tissues. This results in excessive tiredness, leg swelling, shortness of breath, and limited ability to exercise.
- Congenital Heart Disease
- Congenital heart disease involves an individual born with some sort of heart defect. This defect could be minor or serious. The defect could be in the heart valves, heart walls, issues with the muscles, or bad connections among certain blood vessels. Symptoms include shortness of breath and problems with exercise. Some instances of this condition require no action; however, others require doctor visits for life. In order to gain disability protection, an individual would need to prove they have the condition and that it limits them in a major life activity. Based on severity, congenital heart disease will be able to earn disability protection.
- Cardiomyopathy
- The measurable deterioration of the heart muscles and their ability to contract, which leads to heart failure. Symptoms are normally not apparent and come in the form of swollen legs and shortness of breath. Eventually, an individual may need a mechanical implant or a heart transplant. Depending on the limitations that result from this condition, an individual may be able to obtain disability protection.
- Atherosclerosis
- Atherosclerosis is a vascular disease in which the artery wall thickens due to an accumulation of white blood cells. It appears to look like fatty streaks and can typically go unnoticed until the individual suffers from a stroke or heart attack. In some cases, symptoms can include weakness, inability to think straight, difficulty speaking, becoming dizzy, and difficulty walking or standing. Depending on the severity of an individual’s case, this condition may be able to gain disability protection.
- Ischemic Heart Disease (IHD)
- IHD is when one or more of an individual’s coronary arteries is narrowed, obstructed, or constricted due to vasospasm, interfering with the normal flow of blood to the heart muscle. Symptoms typically include chest pain that occurs regularly with activity, after eating, or at other predictable times. Based on the impact this condition has on an individual’s ability to perform daily activities, this condition may be able to gain disability protection.
- Arrhythmias (Irregular Heartbeat)
- Irregular heartbeat is a condition in which the heart beats too fast or too slow. This condition cannot be related to reversible causes such as electrolyte irregularities or digitalis glycoside, or antiarrhythmic drug toxicity. Symptoms can include lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, or chest pain. Depending on the frequency of symptoms, severity of symptoms, and limitation on performing major life activities, this condition can gain disability protection.
- Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)
- PVD is an impairment that affects either the arteries or the veins in the extremities, particularly the lower extremities such as the legs. Symptoms vary greatly from person to person, but can include painful cramping, achiness, fatigue, burning, gangrene, reduced hair growth, severe burning pain in your toes, leg cramps, etc. The severity of the condition will determine whether or not PVD is able to earn disability protection.
- Edema
- Edema is swelling that is usually dense and feels firm due to the presence of increased connective tissue and can stimulate organ swelling. It typically results in inflexibility. One type of edema is Lymphedema, which is edema of the extremities, and at its worst, it is called Elephantiasis. This results in in a restriction of one’s ability to walk due to the swelling of the limbs. Edema will require a case-by-case analysis to determine where there is a limit on a major life activity in order to gain disability protection.
- Gastrointestinal Hemorrhage
- This condition can result in Hematemesis (blood vomiting), melena (tarry stools), or hematochezia (bloody stools). Some individuals require transfusions of 2 units of blood multiple times during a 6-month period. Symptoms of gastrointestinal hemorrhage are:
- Hemodynamic instability
- Pale skin
- Diaphoresis (profuse perspiration)
- Rapid pulse
- Low blood pressure
- Postural hypotension (pronounced fall in blood pressure)
- Syncope (fainting)
- This condition has the possibility of gaining disability protection, but it is dependent on an individual’s case and its severity.
- Hepatorenal Syndrome
- Hepatornal syndrome is defined as functional renal failure associated with chronic liver disease in the absence of underlying kidney pathology. Many forms of this syndrome are fatal, however, slower onset forms result in an elevation of serum creatinine marked by sodium retention. Disability protection will rely on the limitations that result from suffering due to this condition.
- Hepatic (Liver) Dysfunction
- Hepatic Liver Dysfunction is when the liver fails and is no longer able to perform its functions. There are two types of hepatic failures, acute and chronic. Acute liver failure strikes fast and can occur within a few days or weeks without warning. Chronic liver failure happens slowly over months or years and is typically associated with cirrhosis. Liver failure is typically the result of a combination of genetics and environmental factors. Symptoms usually include nausea, fatigue, diarrhea, jaundice, weight loss, itching, and edema. This condition is likely to gain disability protection due to the seriousness of liver failure
- Episcleritis
- Episcleritis is an inflammatory disease affecting the part of the eye called the episclera. The episclera is the white part of an eye. Individuals who suffer from this condition experience it frequently. Treatment is meant to decrease discomfort. Symptoms include mild eye pain, redness, and watery eyes. Episcleritis gaining disability protection is dependent on severity and frequency of the attacks.
- Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
- PSC is a disease of the bile ducts that results in a restricted bile movement. This decreased movement can cause major issues with the liver such as cancer and cirrhosis. While many with PSC show no symptoms, in some cases an individual will suffer from severe itching, severe fatigue, jaundice, conjugated bilirubin, malabsorption, hepatomegaly, and portal hypertension. Depending on the severity of an individual’s case, this condition may earn disability protection.
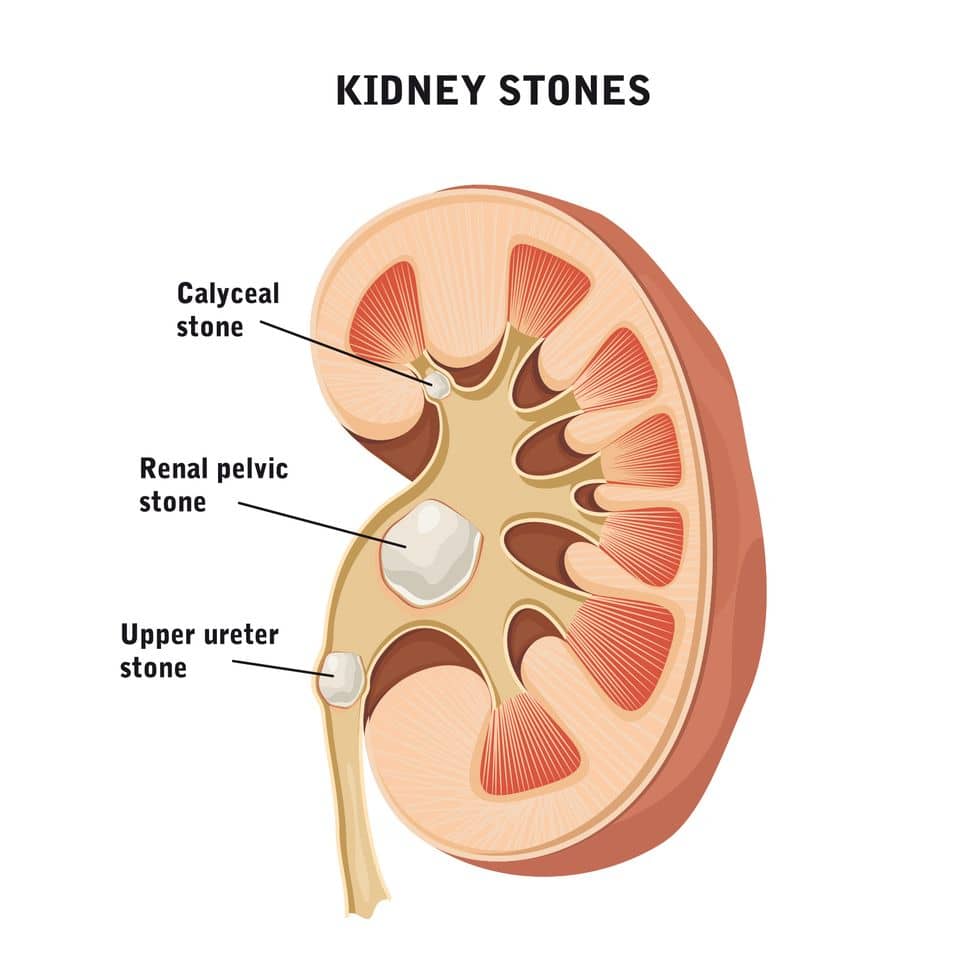
- Kidney stones
- Kidney stones are a buildup of solid material, which is formed within the kidneys. They vary in size, with the smaller ones harmlessly passing through the urinary system, but the larger ones can cause severe discomfort. Symptoms include abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, and severe pain upon the exit of the stone. Depending on the frequency, size, and difficulty of the stones, this condition may gain disability protection.
- Pyoderma Gangrenosum
- Pyoderma gangrenosum is a condition where deep ulcers form on the legs. These ulcers are usually necrotic and look like bug bites in the earlier stages. The wounds rarely lead to death, but they do cause pain and scarring. Furthermore, they can be large and look very disturbing. Depending on an individual’s condition, this condition can gain disability protection.
- Chronic Liver Disease
- Chronic liver disease is a disease characterized by liver cell necrosis, inflammation, or scarring (fibrosis or cirrhosis) due to any cause that persists for more than 6 months. Depending on the underlying causes and symptoms, this condition will gain disability protection.
- Portal Hypertensive Gastropathy
- Portal hypertensive gastropathy is a change in the mucosa of the stomach in patients with portal hypertension. This is one of the most common causes of cirrhosis of the liver. Symptoms can be stomach bleeding, blood vomiting, or melena. If an individual suffers from severe enough symptoms, they may be able to earn disability protection.
- Hydrothorax
- Hydrothorax is an accumulation of serious amounts of fluid in the pleural cavity. This condition is difficult to manage in end-stage liver failure and usually does not respond to therapy. Treatment of this condition is extremely difficult, because it is typically the result of an alternate underlying condition that must be resolved first. If this condition limits a major life activity, it is likely to get disability protection.
- Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca Syndrome (Dry Eye Syndrome)
- Dry eye syndrome is the condition of having dry eyes. This condition can be mild and occasional, or severe and constant. Symptoms include irritation, redness, discharge, easily fatigued eyes, and blurred vision. There are many possible causes, including pregnancy, LASIK surgery, allergies, and more. Depending on the frequency and severity of an individual’s symptoms, this condition will be given disability status.
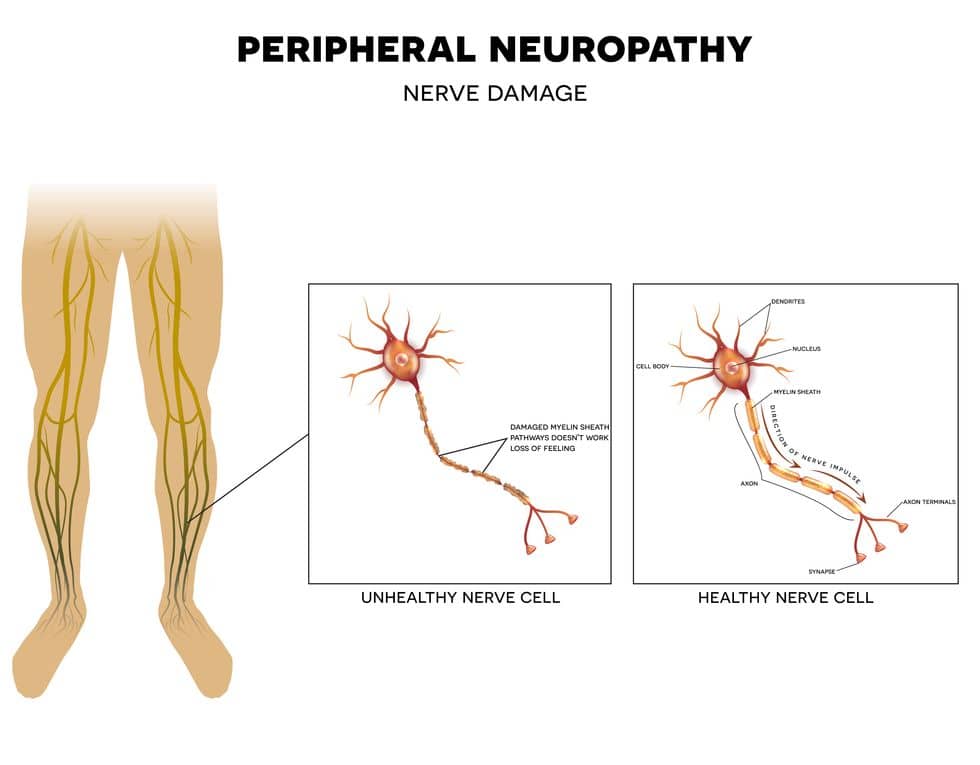
- Peripheral Neuropathy (PN)
- PN is damage or a disease that impacts the nerves. This damage results in sensation impairments, movement restrictions, poor gland or organ function, or impact on other portions of the body depending on what nerves are impacted. This condition can also result in painful cramps, muscle twitching, and changes to hair, skin, and nails. Depending on the severity of PN, it will earn disability status.
- Sjogren’s Syndrome (SS)
- SS is a long-term autoimmune disease where the moisture producing glands of the body begin to dysfunction. This leads to chronic dryness in the mouth, eyes, skin, and vaginal area. It also causes a chronic cough, exhaustion, and muscle and joint pains. SS can also damage and impact the body organs and cause other negative symptoms. Depending on the severity of an individual’s symptoms, this condition will get disability protection.
- Vasculitis
- Vasculitis is a group of disorders that destroy blood vessels by inflammation. Symptoms vary depending on which body system is being affected. Symptoms include fever, weight loss, myositis, arthritis, headache, stroke, visual loss, hypertension, bloody cough, abdominal pain, and glomerulonephritis. Depending on the severity and underlying causes of this condition, it will be considered a disability.
- Primary Biliary Cirrhosis (PBC)
- PBC is an autoimmune disease of the liver. It is characterized by the slow progressive destruction of the bile ducts of the liver. When these ducts are destroyed, harmful toxins build up in the liver, causing damage. This can eventually turn into fibrosis, scarring, and cirrhosis. Individuals with this disease experience severe fatigue, itching, jaundice, and weakened bones. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, this condition will gain disability protection.
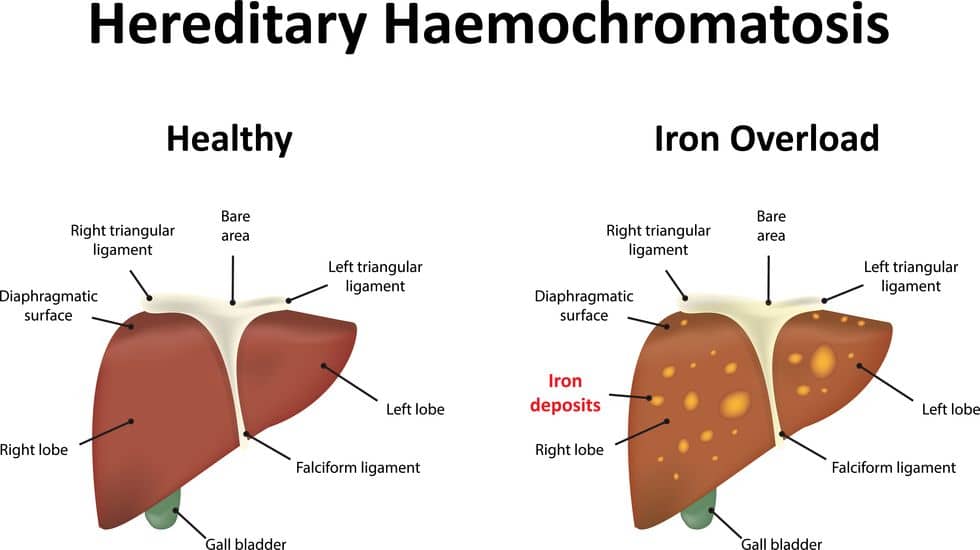
- Hemochromatosis
- Hemochromatosis is when there is too much iron in an individual’s blood. The most common cause is the result of undergoing too many blood transfusions. The danger of this condition is that it may cause cirrhosis, diabetes, cardiomyopathy, arthritis, testicular cancer, and joint/bone pain. Depending on the severity of an individual’s symptoms, this condition will earn disability protection.
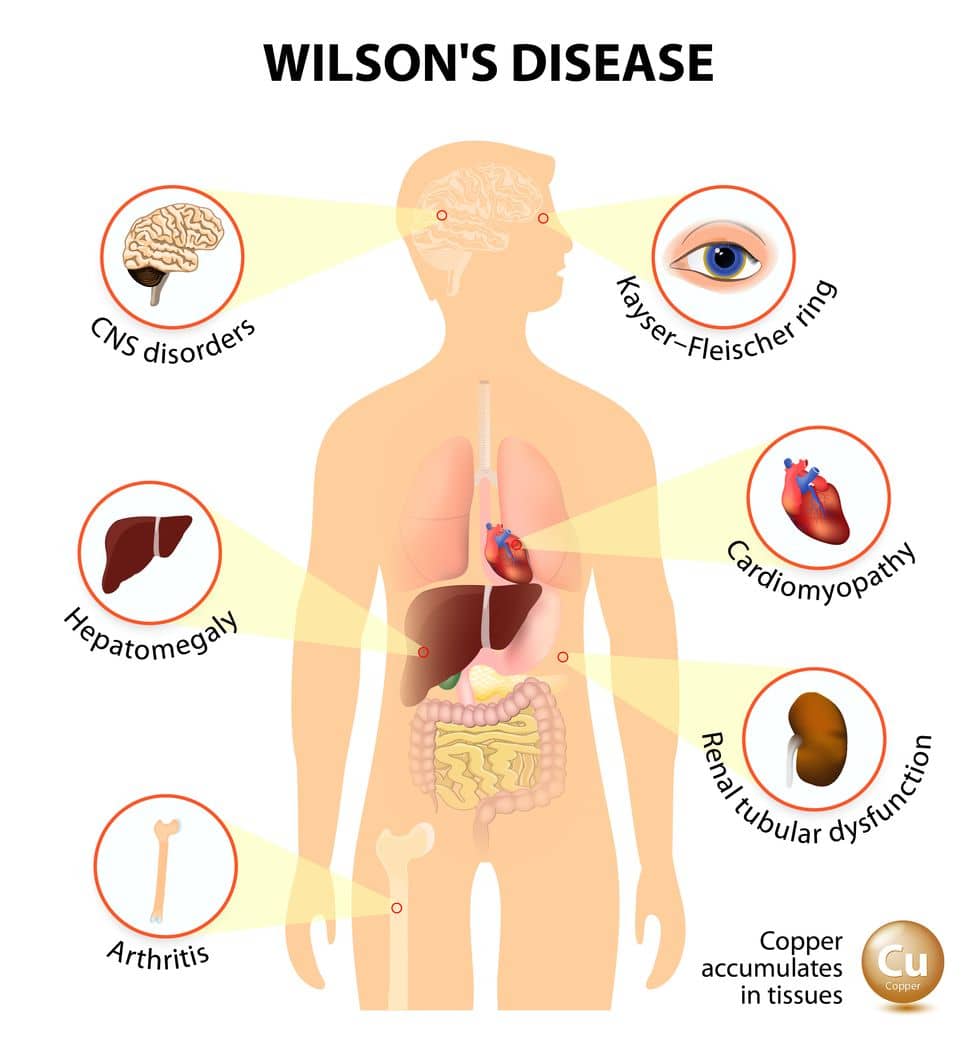
- Wilson’s Disease
- Wilson’s Disease is a genetic disorder in which copper accumulates in body tissues. This disease manifests in neurological or psychiatric symptoms and liver disease. Overally, symptoms include slowed movements, lack of balance, cogwheel rigidity, slurred speech, tremors, seizures, and migraines. Depending on an individual’s symptoms, they will be able to qualify for disability protection.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
- CKD is a progressive loss of kidney function over a period of months or years. Symptoms include blood pressure, urea, hyperkalemia, anemia, edema, hyperphosphatemia, hypocalcemia, metabolic acidosis, and iron deficiency anemia. Depending on the interference with major life activities, this disease can gain disability protection.
- Renal Osteodystrophy
- Renal osteodystrophy is bone degeneration resulting from chronic kidney disease due to the kidney’s failure to maintain a certain level of minerals, hormones, and vitamins for bone structure and function. This results in severe bone pain, which prevents both physical and mental activities. Due to the great interference with daily life activities by this condition, individuals who suffer from this condition will get disability protection.
- Hypervolemia (Fluid Overload Syndrome)
- Hypervolemia is a medical condition where too much fluid builds up in the body system leading to excess sodium in the system. This extra sodium leads to increases in extracellular body water, causing congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure. Symptoms include liquid buildups in various parts of the body, swelling of the arms and legs, difficulty breathing, and difficulty sleeping. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, this condition may gain disability protection.
- Hypertensive Nephropathy
- Hypertensive nephropathy is a medical condition that refers to damage in the kidneys from chronic high blood pressure. This results in pink material accumulating in the wall of small arteries, causing thickening of their walls and narrowing of the lumina. Depending on the severity of the symptoms and subsequent illnesses, this condition will gain disability protection.
- Diabetic Nephropathy
- Diabetic nephropathy is a progressive kidney disease caused by damage to the capillaries in the kidney. This illness is classified by nephrotic syndrome and diffuse scarring of the glomeruli. Symptoms can take 5 to 10 years to fully develop and come in the form of exhaustion, headaches, general feeling of illness, nausea, vomiting, lack of appetite, itchy skin, and leg swelling. Depending on the severity and impact of the symptoms, this condition can gain disability protection.
- Alport Syndrome
- Alport syndrome is a genetic disorder that relates to kidney disease. This syndrome is nothing more than an inherited defect that impacts the normal function of parts of the body. Symptoms include bloody urine, hearing loss, leiomyomatosis, and eye changes. This condition usually appears in children, but can impact adults. If an adult is affected by this syndrome and prevented from going to work, this condition will gain disability protection.
- Thalassemia
- Thalassemia is an inherited blood disorder that causes abnormal hemoglobin formation. This results in the improper oxygen transport and destruction of red blood cells. This can result in iron overload, infection, enlarged spleen, slowed growth rates, heart problems, and bone deformities. Some of the more serious types of thalassemia are those impacting the bone marrow. In this case, the bone marrow is not properly producing red blood cells, which leads to expansion of the bone marrow, creating deformed bone structures. This also weakens the integrity of the bones, making them more prone to breaking. In order to gain disability protection, individuals must get their particular case of Thalassemia evaluated.
- Hereditary Spherocytosis
- Hereditary spherocytosis is an autosomal abnormality that is caused by mutation in one’s genes, allowing for erythrocytes to change shape. This interferes with the cell’s ability to travel from the arteries to the capillaries. Furthermore, this misshapenness causes red blood cells to be more prone to rupture. Symptoms include anemia, hypoxia, and abdominal pain that can lead to the removal of the spleen or gallbladder. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, this condition can gain disability protection.
- Thrombosis or Hemostasis
- Both of these conditions encompass clotting and bleeding disorders (congenital or acquired). The disorders are characterized by abnormalities in blood clotting that result in hypercoagulation or hypocoagulation. Depending on the severity of the caused conditions and their symptoms, they may be able to gain disability protection.
- Hemophilia
- Hemophilia is mostly an inherited disorder that prevents blood clotting, which is a process necessary to stop bleeding. Depending on the severity of the condition, symptoms can be internal bleeding or external bleeding. The frequency of the bleeding varies from person to person. There can be episodes of spontaneous bleeding, as well as bleeding between the joints. This leads to joint damage, pain in muscles and joints, transfusion infection, and intracranial hemorrhage. This condition can be very debilitating and requires individuals to get many blood transfusions depending on the severity. This condition will gain disability protection if the symptoms are severe enough.
- Von Willebrand Disease (VWD)
- VWD is the most common blood-clotting disorder; however, the only truly life-threatening version is type 3 VWD. In type 3 VWD there is next to no ability for the blood to clot, which leads to very serious internal bleeds that can cause a lot of damage. Depending on the type and severity of VWD, individuals may gain disability protection. Factors to consider in making this determination would be frequency, severity, and debilitation.
- Thrombocytopenia
- Thrombocytopenia refers to a disorder where there is a decreased number of platelets in the blood. While many patients exhibit no symptoms, some show spontaneous external bleeding or internal bleeding in the form of bruises. Furthermore, some individuals suffer from weakness and fatigue regardless of blood loss. This condition has potential to gain disability protection, but it is heavily reliant on the severity of the symptoms.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
- MDS is a medical condition that is classified by an ineffective production of all blood cells. This condition develops into severe anemia that may require blood transfusions in order to remedy. Symptoms come in the form of anemia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia. Individuals will suffer from shortness of breath, chest pain, increased infections, and reduced bleeding, depending on the resulting condition. Depending on the condition and its severity, MDS will be able to get disability protection.
- Aplastic anemia
- Aplastic anemia is a rare disease where the bone marrow and the hematopoietic stem cells are damaged. This results in a deficiency of all the blood types. This then severely weakens the body overall, causing anemia, pallor, malaise, low platelet counts, bruising, and increased risk of infection. Depending on the severity of the condition and resulting conditions, aplastic anemia will be able to gain disability protection.
- Polycythemia
- Polycythemia is a disease where there is an overproduction of red blood cells, increasing the proportion of red blood cells in the body. This imbalance throws off the balance of blood cells, causing issues of hyperviscosity or thrombosis. This disease is resolved through removal of the blood in a process called venesection. Depending on the frequency of venesections and severity of any other symptoms, this condition will gain disability protection.
- Ichthyosis
- Ichthyosis is a genetic skin disorder. All victims of ichthyosis have dry, thickened, flaky skin. This condition makes the skin look similar to fish scales. The severity of the symptoms varies greatly from mild to non-existent to life-threatening. Depending on the severity of the condition and whether the skin lesions persist for at least 3 months, despite continuing treatment as prescribed, determines this disorder’s ability to gain disability protection.
- Dermatitis – (psoriasis, dyschidrosis, atopic dermatitis, exfoliative dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis)
- Dermatitis is a group of diseases that result in inflammation of the skin. Symptoms are often itchy, red skin with small blisters. In some cases, the area of skin that was affected can harden and may become thick. The severity of the attacks and their frequency will determine whether this condition gains disability protection. Typically, those that qualify for disability protection suffer from extensive skin lesions that persist for at least 3 months, despite continuing treatment as prescribed.
- Scleroderma
- Scleroderma is a hardening of the skin that in severe cases will impact the internal organs. Depending on the site of the disease, it can have many different symptoms. Just some of the many symptoms include ulcers, irregular heartrate, fainting, heart failure, indigestion, bloating, sicca syndrome, persistent cough, chest pain, joint pain, loss of motion, carpal tunnel syndrome, kidney failure, facial pain, etc. Depending on an individual’s symptoms, this condition will likely qualify for disability protection.
- Hyperglycemia
- Hyperglycemia can be both chronic and acute. This condition involves long-standing abnormally high levels of blood glucose in the body. This disrupts the nerve and blood vessel functions. This condition, if not treated successfully, can lead to a number of other problems. Symptoms range from frequent hunger to blurred vision, fatigue, weight loss, dry mouth, itchy skin, seizures, etc. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, this condition will gain disability protection.
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Diabetic ketoacidosis is an acute potentially life-threatening complication where the chemical balance of the body becomes dangerously acidic, resulting in severe insulin deficiency. This can result in vomiting, dehydration, gasping, confusion, and coma. Treatment is typically done through intravenous fluids. Depending the frequency and severity of this condition, individuals will gain disability protection.
- Myasthenia Gravis (MG)
- MG is a neuromuscular disease that leads to varying levels of muscle weakness through the body. Depending on which body part is affected, it can lead to significant difficulty with speaking, swallowing, breathing, motor weakness of muscles and extremities. Depending on the severity and impacted body system, this condition will get disability protection.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS), Lou Gehrig’s Disease
- ALS is a disorder that involves the death of the neurons that control voluntary muscles. This leads to a stiffening of the muscles, muscle twitching, and gradually increasing muscle weakness. This eventually results in difficulty speaking, swallowing, and eventually breathing. This condition is very likely to gain disability protection.
- Cerebral Palsy
- Cerebral palsy is a permanent movement disorder. It usually appears in early childhood and is classified by poor coordination, stiff muscles, weak muscles, and tremors. There can also be issues with vision, hearing, swallowing, and speaking. Sometimes it can also lead to difficulty with thinking or reasoning and cause seizures. Depending on the severity of the symptoms and the damage to the body, this condition will get disability protection.
- Poliomyelitis (Polio)
- Polio is an infectious disease cause by the poliovirus. It results in progressive muscle weakness that eventually results in an inability to move. Normally, it impacts the legs, but can also involve head, neck, and diaphragm muscles. Other individuals can sometimes only suffer from headaches, neck stiffness, and pains in the arms and legs. Depending on the severity and progression of the disease, this condition will gain disability protection primarily due to loss of movement.
- Pernicious Anemia
- Pernicious anemia occurs when the body loses red blood cells due to an inability to use B12 vitamins. Symptoms can include desire to eat ice or other non-food things, diarrhea, fatigue, pale skin, focus problems, and shortness of breath. Long-term low vitamin B12 deficiencies can cause confusion, depression, loss of balance, and numbness. Depending on an individual’s symptoms, this condition can get disability protection.
- Huntington’s Disease (HD)
- HD is an inherited disorder that results in the death of brain cells. Earliest symptoms include subtle problems with mood, lack of coordination, and jerky body movements. Eventually, this leads to a loss of physical abilities and a digression into dementia. Depending on the severity and rapidity of these symptoms, individuals can gain disability protection.
- Friedreich’s Ataxia
- This condition is a disease that causes slow progressive damage to the nervous system. Symptoms manifest in the form of poor coordination, heart disease, scoliosis, and diabetes. Furthermore, it can cause fatigue and eventually lead to the need for a wheelchair. Depending on an individual’s symptoms, this condition will get disability protection.
- Syringomyelia
- Syringomyelia is when a cyst or cavity forms within the spinal cord and grows over time, destroying the spinal cord. The damage results in pain, paralysis, loss of movement, weakness, and stiffness. In certain severe cases, individuals will suffer from extreme cape-like pain across the back, shoulders, and extremities. Depending on an individual’s symptoms, this condition will gain disability protection.
- Systemic Vasculitis
- Systemic vasculitis is an inflammation of blood vessels. It may occur acutely in association with adverse drug reactions, certain chronic infections, and occasionally malignancies. The different types are: Polyarteritis Nodosa, Takayasu’s Arteritis (aortic arch Arteritis), Giant Cell Arteritits (Temporal Arteritis), Wegener’s Granulomatosis. Depending on the severity of an individual’s symptoms, this condition may gain disability protection.
- Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
- Systemic sclerosis is an autoimmune disease of the connective tissue. Symptoms include thickening of the skin caused by accumulation of collagen and small arteries. The severity of the condition depends on what body system is impacted. Sometimes it is limited to the face, hands, and feet. The more serious version impacts the organs and more of the skin. The survival rate is usually very high, but goes down if important organs like the lungs, heart, or kidneys are being attacked. Depending on the severity of an individual’s condition, it will get disability protection. Other related diseases of this condition that can, in extreme cases, lead to disability protection are:
- Raynaud’s Phenomenon
- CREST Syndrome
- Calcinosis
- Esophageal Dysmotility
- Sclerodactyly
- Telangiectasia
- Whipple’s Disease
- Whipple’s disease is a rare infectious disease that is also considered a gastrointestinal disorder. The primary symptom is malabsorption, but it can also affect any part of the body. Other symptoms include diarrhea, abdominal pain, weight loss, and joint pains. Depending on the severity and types of symptoms, individuals can qualify for disability protection.
- Behcet’s Disease
- Behcet’s disease is a rare condition that often results in ulceration in the mucous membrane. Symptoms include painful ulcerations in the genitals, oral lesions, and sores within the mouth. It can also affect the ocular system, bowels, lungs, musculoskeletal, neurological, and cardiac system. Depending on the severity of the condition and the symptoms, behcet’s disease may be able to gain disability protection.
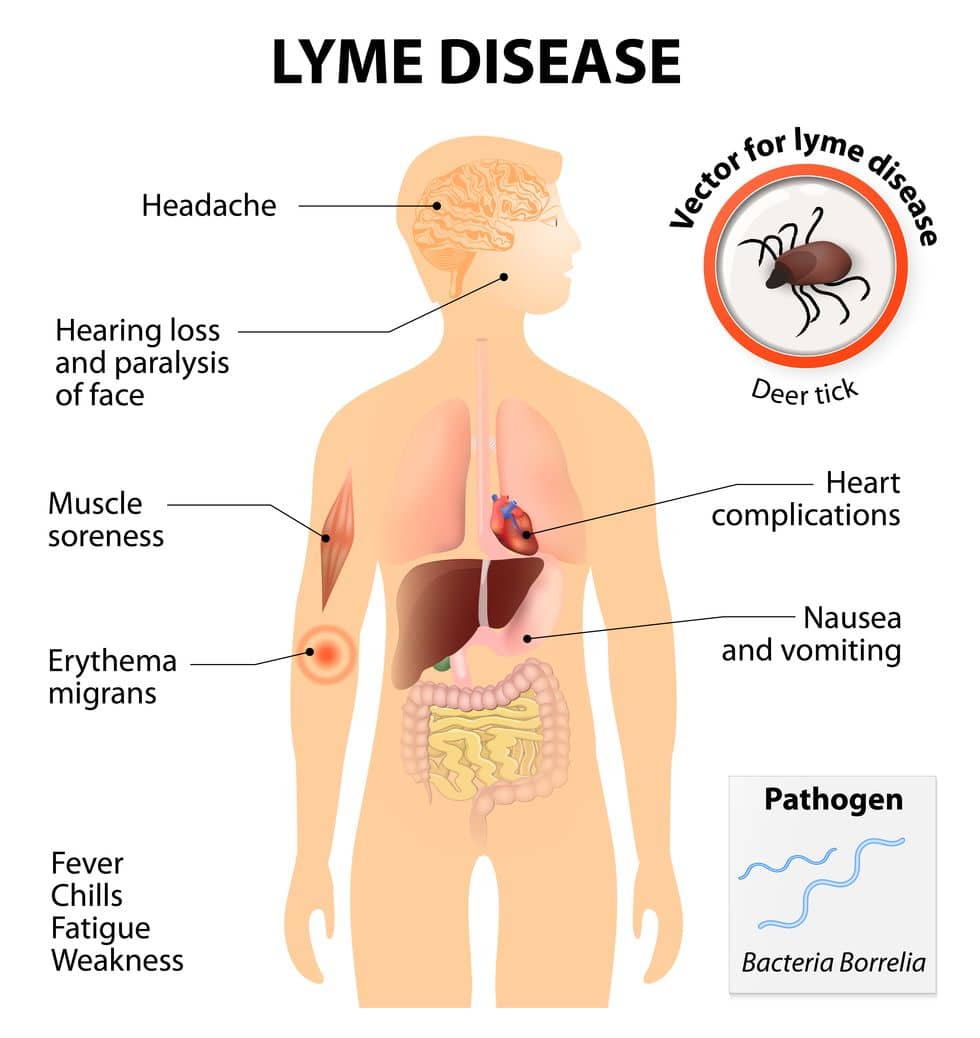
- Lyme Disease
- Lyme disease is an infectious disease cause by a bacterium of the Borrelia type. This disease is usually caused by tick bites and onset occurs about a week after the initial bite. Symptoms include fever, headache, and exhaustion. If left untreated for a long period, it will develop into loss of movement in face, joint pains, and severe headaches. There can also be long term spikes of joint pain and swelling. Some cases result in joint pain and memory problems for a period of at least six months. Depending on the symptoms, lyme disease may earn disability protection.
- Pleuritis (Pleurisy)
- Pleuritis is an inflammation of the pleurae, which is a membrane surrounding the lungs. This can be caused by viral infections or other reasons. Symptoms include sharp pain when breathing, chest pain, dry cough, shortness of breath, sore throat, and painful and swollen joints. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, certain individuals may gain disability protection.
- Pulmonary Fibrosis
- Pulmonary fibrosis is a scarring of the lungs, which leads to serious breathing problems. Scars form as result of excess connective tissue, which thickens on the lung’s walls and causes a reduced oxygen supply. This can lead to perpetual shortness of breath, chronic cough, fatigue, chest pain, and loss of appetite. Depending on the severity of the condition, pulmonary fibrosis will gain disability protection.
- Myocarditis
- Myocarditis is an inflammation of the heart muscle. Symptoms can vary and include chest pain, congestive heart failure, palpitations, sudden death, and fever. Myocarditis can be the result of infections, toxins, physical agents, and immunological responses. Depending on severity and result of symptoms, it can gain disability protection.
- Pericarditis
- Pericarditis is an inflammation of the fibrous sac surrounding the heart. A common characteristic is chest pain, and the disease can be acute or chronic. This condition can be cause by infections, heart trauma, and unknown causes. Disability protection will rely heavily on the symptoms that result from this condition.
- Radiculopathy
- Radiculopathy is a set of conditions in which the nerves are affected and do not work properly. The problem typically occurs at or near the root of the nerve shortly after it exits from the spinal cord. Symptoms depend on what nerves are impacted, since the pain can result all over the body. However, the pain is typically classified by numbness, weakness, and pain. Depending on the severity of the symptoms and the manner in which they occur, this condition may gain disability protection.
- Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES)
- CES is a serious neurological condition where there has been damage to the cauda equine, which causes the loss of function of the lower motor area. Symptoms include severe back pain, saddle anesthesia, bladder/bowel dysfunction, sciatica-type pain, weakness of the muscles, Achilles ankle reflex, sexual dysfunction, and gait disturbance. This condition is very likely to gain disability protection.
- Felty’s Syndrome
- Felty’s syndrome is essentially a combination of rheumatoid arthritis, splenomegaly, and neutropenia. This condition usually affects those between 50-70 years old. Symptoms include painful, stiff, swollen joints, enlarged spleen, and decreased white blood cell count. These are just a few of the symptoms that may occur. Depending on the symptoms that occur, this condition will gain disability protection.
- Nocardiosis
- Nocardiosis is an infectious disease impacting either the lungs or the whole body. It is typical in men with weaker immune systems. Symptoms vary widely depending on what body system or systems are affected. Symptoms can include chest pain, cough, confusion, seizures, chronic subcutaneous infection, fever, and cutaneous lesions. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, this condition will be given disability protection.
Medical Conditions
Cancer is a group of diseases that involve abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. Not all tumors are cancerous. Signs of cancer are lumps, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, change in bowel movements, unexplained weight loss, etc. While tobacco causes 22 percent of cancer-related deaths, there are many poor lifestyle habits that may cause cancer. There are many kinds of cancer and many treatments.
Recently, it has been realized that cancer patients face many road blocks when it comes to their employment opportunities. Employers have biases about a person’s ability to work before and after cancer, regardless of their prognosis and whether the cancer is still active. It is for these reasons that employment laws have decided to see cancer as a condition that should easily gain disability protection. This means that employment law will likely consider any patient with active cancer, or cancer that is in remission, as having disability protection. Essentially, any patient with a history of cancer will be protected in the employment context.
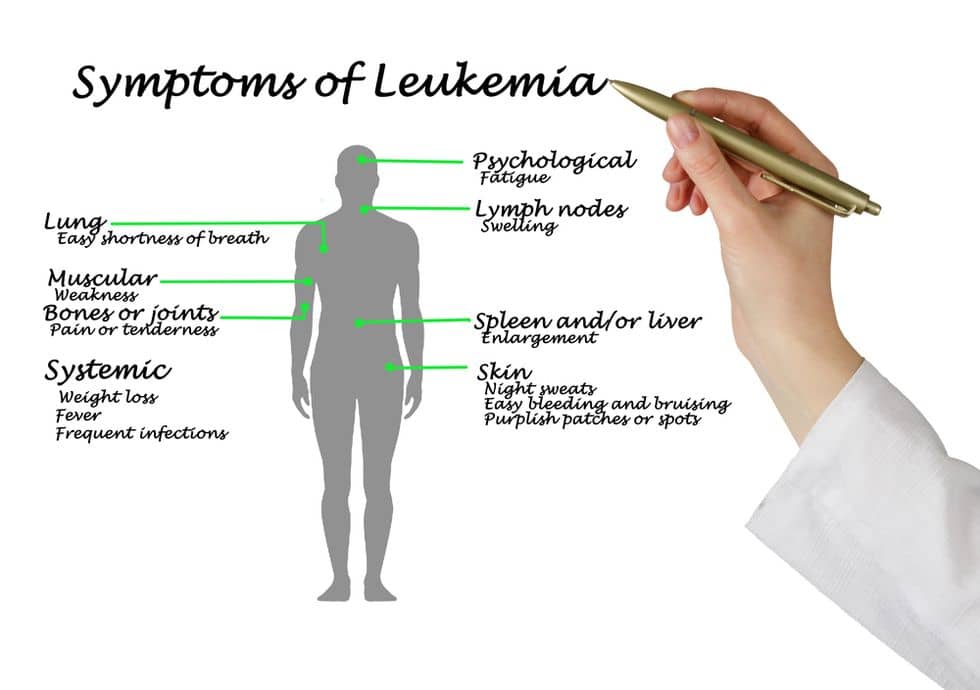
- Leukemia
- Leukemia is a type of cancer that starts in the blood, but can transition throughout the body into vital organs. Unlike standard cancer, it usually does not involve tumors. It is characterized by a high number of undeveloped white blood cells. Symptoms include bleeding, bruising, exhaustion, fever, and increased risk of infection. There are two categories of leukemia, acute and chronic. Acute leukemia is quick developing and attacking, while chronic leukemia is slow developing and slow attacking.
- Bone Tumors
- Bone tumors occur when bone cells divide without control, forming a mass of tissue. The five-year survival rate of this condition is currently 67 percent. Tumors can either be benign or cancerous. Usually, individuals with this condition tend to experience increasing pain, fatigue, fever, weight loss, anemia, and unexplained bone fractures.
- Brain Cancer
- Brain cancer is when tumors both malignant and benign begin to grow in the brain. These growths in the brain lead to seizures, sleepiness, confusion, and behavioral changes. Sometimes there can be growths in the brain that are the result of cancer cells traveling from other cancers in the body through the blood. This tends to result from breast cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer, and colon cancer.

- Breast Cancer
- Breast cancer is a cancer that develops from the breast tissue. This can cause a lump in the breast or a change in the breast shape. Sometimes it can cause fluid to excrete from the nipple and growth of red scaly patches of skin. There have also been symptoms involving bone pain, swollen lymph nodes, and shortness of breath. It is important to check the breasts for lumps as much as possible. Inflammatory breast cancer can have additional symptoms like itching, swelling, nipple inversion, warmness, and redness through the breast.

- Burkitt Lymphoma
- Burkitt lymphoma is one of the deadliest forms of cancer that starts in immune cells called B-cells and weakens the immune system. Long-term survival can be achieved, but with intensive chemotherapy. There are three main types of Burkitt lymphoma: the endemic variant, sporadic type, and the immunodeficiency type. The endemic variant is common among children living in locations where malaria exists. The sporadic type is the most common type and tumor cells have a similar appearance to those of cancer cells. The final form is usually associated with HIV infection or occurs post-transplant.
- Cervical Cancer
- Cervical cancer takes place in the lower part of the uterus. It is the most common cancer in women, but is often found early due to regular testing in the United States. If found early, it can be cured with little or no trouble. Long-lasting infections like HPV tend to cause almost all cases of cervical cancer.

- Colorectal Cancer
- Colorectal cancer is cancer of the colon or rectum. Signs of this type of cancer may include blood in the stool, a change in bowel movements, weight loss, and chronic fatigue. Risk factors include smoking, obesity, and lack of physical activity.
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Hodgkin’s Lymphoma is a type of lymphoma, a cancer of the lymphatic system. This system acts as a filter and is also responsible for producing white blood cells. Symptoms include fever, night sweats, and weight loss. There are often enlarged lymph nodes in the neck, under the arm, or in the groin. These enlargements are not known to be painful. Other symptoms include itchy skin, pain following alcohol consumption, back pain, red patch skin, and easy bleeding due to low platelet count.
- Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
- Non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma is a group of blood cancers that includes all types of lymphoma except Hodgkin’s lymphoma. It is a type of cancer that occurs when the white blood cells become abnormal and stop protecting the body. Symptoms can be fever, night sweats, weight loss, itchiness, chest pain, and bone pain. There are some forms that are slow growing, while other grow more quickly.
- Liver Cancer
- Cancer of the liver. Symptoms include abdominal mass, abdominal pain, yellow skin, nausea, or liver dysfunction. Liver cancer can be caused by cirrhosis due to the hepatitis virus or alcohol. Liver cancer is one of the more common types of cancer and the second most common cause of cancer-related deaths.

- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Hepatocellular carcinoma is the most common type of liver cancer. It is primarily caused by hepatitis b or c, metabolic toxins, or aflatoxin. Depending on tumor size and stage, different treatment approaches will be taken. Symptoms include yellow skin, fluid buildup in abdomen, easy bruising, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or exhaustion.
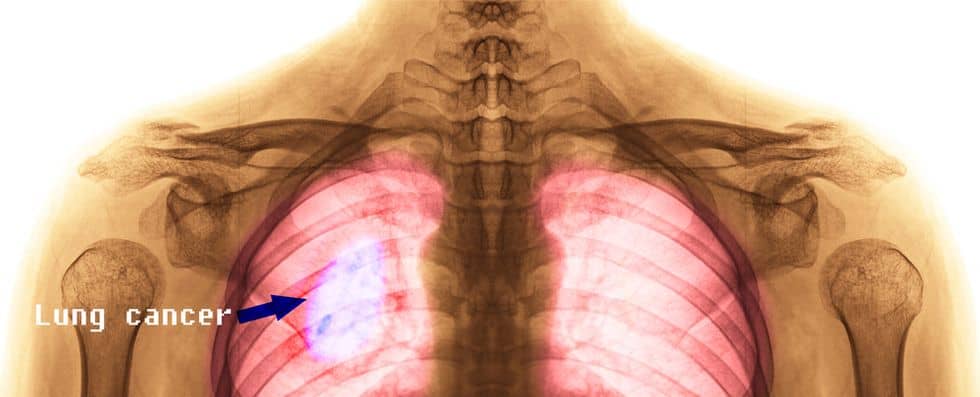
- Lung Cancer
- Lung cancer, also known as lung carcinoma, is a malignant tumor that is characterized by an uncontrolled growth that occurs in the lung tissues. This cancer can spread beyond the lung to other parts of the body. There are two main types, small-cell lung carcinoma and non-small-cell lung carcinoma. The most common symptoms are coughing blood, weight loss, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Most cancer is caused by long-term tobacco smoking, but can also result from pollution, genetic factors, and secondhand smoke. In order to prevent this cancer, the best solution is to try and avoid smoking.
- Melanoma/Skin Cancer
- Melanoma is a type of cancer that contains pigmented cells called melanocytes. This condition occurs in the skin, but can very rarely occur in the mouth, intestines, or eyes. Sometimes melanoma develops from a mole, which increases in size, irregular edges, change in color, itchiness, or skin break down. The primary cause of melanoma is ultraviolet light exposure in those with low levels of skin pigment. Sunscreen and avoiding UV light may prevent melanoma. Typical resolution involves surgical removal.
- Meningioma
- Meningioma is a tumor that forms on membrane that covers the brain and spinal cord just inside the skull or the spine. Typically benign, they can lead to headaches, seizures, blurred vision, weakness, numbness, and speech problems. Treatment can either be surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy.
- Ovarian Cancer
- Ovarian cancer is a cancer that takes place in one or two of the ovaries within women. This cancer may spread to other parts of the body such as the liver. Symptoms of ovarian cancer are bloating, pelvic pain, abdominal pain, trouble eating, urinary issues, fatigue, back pain, constipation, and menstrual changes
- Pancreatic Cancer
- Pancreatic cancer arises when the cells in the pancreas begin to multiply out of control and form a mass. There are many different types of pancreatic cancer, the most common being pancreatic adenocarcinoma. This cancer usually starts from the part of the pancreas that makes digestive enzymes. Typical symptoms include yellow skin, abdominal pain, back pain, unexplained weight loss, light-colored stools, dark urine, and loss of appetite. This cancer rarely occurs before the age of 40. Risk of pancreatic cancer is increased by tobacco smoking, obesity, diabetes, and certain rare genetic conditions.

- Prostate Cancer
- Prostate cancer is when the cells in the prostate gland begin to grow uncontrollably. This type of cancer is the most common form found in males and only affects men. The prostate can increase in size over the years, making it more susceptible. Symptoms and signs of prostate cancer are problems urinating, blood in the urine, blood in the semen, erectile dysfunction, pain in the hips, back pain, chest pain, bone pain, weakness of lower extremities, and loss of bladder or bowel control.
- Testicular Cancer
- Testicular cancer is a cancer that develops in the testicles, which are a part of the male reproductive system. Not all lumps on the testicles are tumors, and not all tumors are cancer. Testicular cancer has one of the highest cure rates. Even if the condition has spread to other parts of the body, it still has an incredibly high survival rate. It is rarely seen before the age of 15, but is it the most common cancer in males aged 20-39. Symptoms include a lump in one testis that may be painful, sharp pain or dull ache in lower abdomen, heaviness in the scrotum, breast enlargement, and lower back pain. While it is not common for this type of cancer to spread to other organs, if it has, there may be shortness of breath, cough, and lumps in the neck.
- Throat Cancer
- Head and neck cancer starts in the lip, oral cavity, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, pharynx, larynx, or parotid glands. This type of cancer usually spreads to the lymph nodes of the neck, which is usually the first sign of the condition. Symptoms include neck pain, bleeding from the mouth, mass in the neck, bad breath, sore tongue, painless ulcers that do not heal, earache, lump in lip, difficulty swallowing food, change in diet, hoarse voice, slurring of speech, enlarged lymph glands, and unusual bleeding in mouth.
- Pituitary Gland Cancer
- The pituitary gland is a small gland near the brain and it is often referred to as the master endocrine gland. This gland releases hormones that affect multiple body functions. A tumor is formed when the healthy cells change and grow out of control. Tumors can be both benign and malignant. Symptoms of pituitary gland cancer include headaches, vision problems, changes in menstrual cycles, infertility, erectile dysfunction, inappropriate production breast milk, Cushing’s syndrome, and enlargement of extremities.
- Stomach Cancer
- Gastric cancer is a disease where the cancer develops on the lining of the stomach. Infection by a bacteria called H. pylori is a common cause of gastric cancer. Early symptoms may include heartburn, upper abdominal pain, nausea, and loss of appetite. Later symptoms may include weight loss, yellowing of the skin, vomiting, difficulty swallowing, and bloody stools. This type of cancer can spread to other parts of the body, particularly the liver, lungs, bones, and lining of the abdomen.
- Parathyroid Cancer
- The parathyroid glands are four tiny glands in the neck near the thyroid gland. These glands produce hormones that help the body use calcium in the blood. While normally the tumors are benign, they can become malignant. Symptoms include weakness, exhaustion, and lumps in the neck. This cancer can also cause calcium surplus diseases.
- Myelofibrosis (Osteomyelofibrosis)
- Myelofibrosis is a rare bone marrow cancer where there is a proliferation of an abnormal clone of hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow, which results in marrow being replaced with scar tissue. Symptoms include enlarged spleen, bone pain, bruising, loss of appetite, fatigue, gout, increased risk of infection, shortness of breath, and cutaneous myelofibrosis.
Mental Disabilities
- Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD) / Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD)
- ADHD is a mental disorder that results in difficulties paying attention, excessive activity, or difficulty controlling behavior that is not appropriate. Individuals who suffer from this condition struggle in school, work, and other tasks that they do not find interesting. In order to treat this condition, there is a combination of counseling, lifestyle changes, and medications. There are varying degrees of severity that can greatly impact the detriment this disorder has on individuals. Some of the symptoms are easily distracted, forgetfulness, difficulty with submitting work on time, struggle to follow directions, difficulty with detail, talking non-stop, poor impulse control, and requiring constant movement. This condition is also often paired with learning disabilities, turrets, mood disorders such as depression, and anxiety disorders. Depending on the severity of the individual’s symptoms, they are likely to gain disability protection.
- Alzheimer’s Disease
- Alzheimer’s is a chronic neurodegenerative disease that usually starts slowly and gets worse over time. It is the cause of 60-70 percent of dementia. Onset of Alzheimer’s can vary greatly, but usually takes between 3-9 years. Early symptoms are short-term memory loss, but as the disease progresses, there are problems with language, disorientation, mood swings, loss of motivation, not managing self-care, and behavioral issues. Eventually the degeneration leads to societal withdrawal and loss of bodily functions. Depending on the severity of the disease and its progression, individuals may be able to earn disability protection.
- Anorexia Nervosa
- Anorexia is an eating disorder that is characterized by a low weight and an extreme fear of gaining weight. This eventually leads to individuals becoming extremely underweight. Individuals who suffer from this condition rarely believe they have a weight problem. Some will exercise, use laxatives, vomit after eating, or take other extreme measures to lose weight. Symptoms vary greatly and mainly involve a restriction in diet, a purging of food after its been eaten, excessive exercise, depression, abdominal distention, halitosis, dry hair and skin, chronic fatigue, and rapid mood swings. This condition can greatly impact the normal flow of a person’s life and depending on the severity, will gain disability protection.

- Anxiety
- Anxiety is an unpleasant state of inner turmoil that is often accompanied by nervous behavior. There is an unpleasant feeling of dread over anticipated events such as the feeling of imminent death. Individuals feel extreme fear, uneasiness, and worry over some event. There are many forms of anxiety and they can often lead to or exacerbate other mental orders, such as panic disorders, depression, OCD, etc. Anxiety can also result in panic attacks, which are strikes of terror that hit without warning. People experiencing a panic attack may believe they are having a heart attack, dying, or going crazy. Depending on the severity of an individual’s symptoms, they may earn disability protection.

- Panic Disorders
- Panic disorder is a type of anxiety disorder that results in recurring panic and anxiety attacks. There can be significant behavioral changes and worries about having more attacks. This condition is often mistaken for another physical illness, such as a heart attack. Usually patients with this disorder tend to go to the emergency room frequently to undergo medical testing. Symptoms during an attack include perspiration, dizziness, dyspnea, trembling, and uncontrollable fear. There can also be hyperventilation, chest pain, nausea, crying, and fainting. Depending on the frequency and the severity of attacks, an individual may earn disability protection.

- Autism
- Autism is a spectrum disorder that results in impaired social interaction, verbal and nonverbal communication, and repetitive behavior. Signs of autism usually occur or are noticed in the first two years of a child’s life. Autism is often characterized by impairments in some respects, while others appear normal. Individuals with autism suffer from an inability to function socially, as they are left unable to understand normal social cues. They are unable to make eye contact while talking and sometimes look in the opposite direction while speaking. There are also complications with communication, where up to half of the autistic population is unable to develop enough speech to meet their communication needs. Additionally, people with autism display signs of repetitive behavior. These can come in the form of hand flapping, head rolling, following self-imposed rigid rules, ritualistic behavior, and self-injury. This condition may gain disability protection depending on the severity of the symptoms.

- Bipolar Disorder
- Bipolar disorder is characterized by extreme mood swings from depression to mania. It can also be called manic depressive disorder. Individuals who suffer from this disorder go through periods of elevated mood and then fall into depressed mood. During the mania or elevated mood, individuals are abnormally energetic, happy, or irritable. During depressed phases, there may be crying, negative outlook on life, or poor eye contact. This condition will also increase the chances of anxiety disorders or substance abuse problems. Symptoms vary depending on the mood the individual is in. For example, during mania, symptoms are rapid speech, easily distracted, racing thoughts, hyper sexuality, or excessive money spending. This must be exhibited to an extent that it interrupts socializing and work. Depressive episodes are characterized by sadness, irritability, anger, loss of interests, excessive or inappropriate guild, hopelessness, and sleeping too much. Depending on the severity of these symptoms, individuals may be able to obtain disability protection.
- Schizophrenia
- Schizophrenia is a brain disorder that distorts the way a person thinks, acts, expresses emotions, perceives reality, and relates to others. An individual cannot tell the difference between what is real and imagined. Symptoms can include false beliefs, unclear confused thinking, hearing voices, reduced social engagement, and emotional expression. Other associated mental problems are anxiety disorders, major depressive illness, or substance use disorder. Depending on the functionality of an individual with schizophrenia, they may be able to earn disability protection.

- Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD)
- SPD is a condition where the brain struggles to communicate with one or more of the five senses. Individuals with this disorder suffer in the performance of productivity, leisure and play, or activities of daily living. They can struggle with exaggerated itchiness, difficulty writing, difficulty in producing force, and difficulty with movement. Depending on the severity of an individual’s condition, they may earn disability protection.
- Somatic Symptom Disorder
- Somatic symptom disorder is a category of mental disorders that come with physical symptoms for which there are no demonstrable organic findings or known physiological mechanisms. Some types of somatic disorders are conversion disorder, illness anxiety disorder, body dysmorphic disorder, pain disorder, and undifferentiated somatic symptom disorder. All of these disorders have real impacts on the patients’ lives. For example, conversion disorder can result in the actual loss of bodily function such as blindness, paralysis, and numbness due to anxiety. Depending on the severity of the disorder and its symptoms, individuals can earn disability protection.













































